Configuring Rapid7 Connectors
Vulnerability scanners examine hosts for known and possible security vulnerabilities. You can connect Stellar Cyber to your existing vulnerability scanner and have Stellar Cyber generate reports on the target hosts scanned.
See Rapid7 for information on configuring a Rapid7 scanner.
Stellar Cyber connectors with the Collect function (collectors) may skip collecting some data when the ingestion volume is large, which potentially can lead to data loss. This can happen when the processing capacity of the collector is exceeded.
Connector Overview: Rapid7
Capabilities
-
Collect: Yes
-
Respond: No
-
Native Alerts Mapped: No
-
Runs on: Sensor
-
Interval: Configurable
Collected Data
|
Content Type |
Index |
Locating Records |
|---|---|---|
|
N/A |
Scans
|
Domain
|
https://<Hostname>:<Port> where <Hostname> and <Port> are variables from the configuration of this connector |
Response Actions
N/A
Third Party Native Alert Integration Details
N/A
Required Credentials
-
Hostname, Username, and Password (of the scanner)
Let us know if you find the above overview useful.
Adding a Rapid7 Connector
To add a Rapid7 connector:
Adding the Connector in Stellar Cyber
To add a new Rapid7 vulnerability scanner connector in Stellar Cyber:
-
Log in to Stellar Cyber.
-
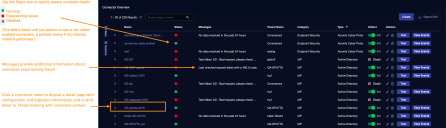
Click System | Integration | Connectors. The Connector Overview appears.
-
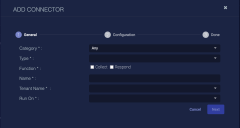
Click Create. The General tab of the Add Connector screen appears. The information on this tab cannot be changed after you add the connector.
The asterisk (*) indicates a required field.
-
Choose Vulnerability Scanner from the Category drop-down.
-
Choose Rapid7 from the Type drop-down.
-
For this connector, the supported Function is Collect, which is enabled already.
-
Enter a Name.
Notes:- This field does not accept multibyte characters.
- It is recommended that you follow a naming convention such as tenantname-connectortype.
-
Choose a Tenant Name. The Interflow records created by this connector include this tenant name.
-
Choose the device on which to run the connector.
-
(Optional) When the Function is Collect, you can apply Log Filters. For information, see Managing Log Filters.

-
Click Next. The Configuration tab appears.
The asterisk (*) indicates a required field.
-
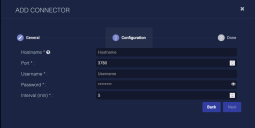
Enter the Hostname. This is the FQDN or IP address of the scanner.
Do not include https in the Hostname.
-
Enter the Port. The default is 3780.
-
Enter the Username to log in to the scanner.
-
Enter the Password to log in to the scanner.
The password should not include non-ASCII special characters.
-
Choose the Interval (min). This is how often the logs are collected.
-
Click Next. The final confirmation tab appears.
-
Click Submit.
The new connector is immediately active and collects logs for the previous 30 days.
Testing the Connector
When you add (or edit) a connector, we recommend that you run a test to validate the connectivity parameters you entered. (The test validates only the authentication / connectivity; it does not validate data flow).
For connectors running on a sensor, Stellar Cyber recommends that you allow 30-60 seconds for new or modified configuration details to be propagated to the sensor before performing a test.
-
Click System | Integrations | Connectors. The Connector Overview appears.
-
Locate the connector that you added, or modified, or that you want to test.
-
Click Test at the right side of that row. The test runs immediately.
Note that you may run only one test at a time.
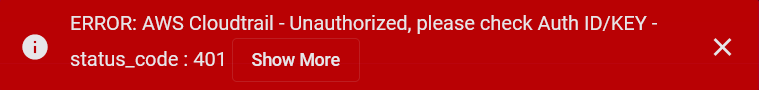
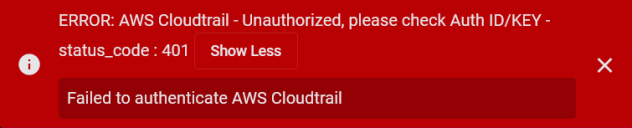
Stellar Cyber conducts a basic connectivity test for the connector and reports a success or failure result. A successful test indicates that you entered all of the connector information correctly.
To aid troubleshooting your connector, the dialog remains open until you explicitly close it by using the X button. If the test fails, you can select the button from the same row to review and correct issues.
The connector status is updated every five (5) minutes. A successful test clears the connector status, but if issues persist, the status reverts to failed after a minute.
Repeat the test as needed.
If the test fails, the common HTTP status error codes are as follows:
| HTTP Error Code | HTTP Standard Error Name | Explanation | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request | This error occurs when there is an error in the connector configuration. |
Did you configure the connector correctly? |
| 401 | Unauthorized |
This error occurs when an authentication credential is invalid or when a user does not have sufficient privileges to access a specific API. |
Did you enter your credentials correctly? Are your credentials expired? Are your credentials entitled or licensed for that specific resource? |
| 403 | Forbidden | This error occurs when the permission or scope is not correct in a valid credential. |
Did you enter your credentials correctly? Do you have the required role or permissions for that credential? |
| 404 | Not Found | This error occurs when a URL path does not resolve to an entity. | Did you enter your API URL correctly? |
| 429 | Too Many Requests |
This error occurs when the API server receives too much traffic or if a user’s license or entitlement quota is exceeded. |
The server or user license/quota will eventually recover. The connector will periodically retry the query. If this occurs unexpectedly or too often, work with your API provider to investigate the server limits, user licensing, or quotas. |
For a full list of codes, refer to HTTP response status codes.
Verifying Ingestion
To verify ingestion:
-
Click Investigate | Threat Hunting. The Interflow Search tab appears.
-
Change the Indices to Scans. The table immediately updates to show ingested Interflow records.