Using AI Investigator
AI Investigator is available as part of an Early Access Program and might not appear in your version of the Stellar Cyber Platform. Contact your account manager to inquire about taking part in the Early Access Program and enabling AI Investigator.
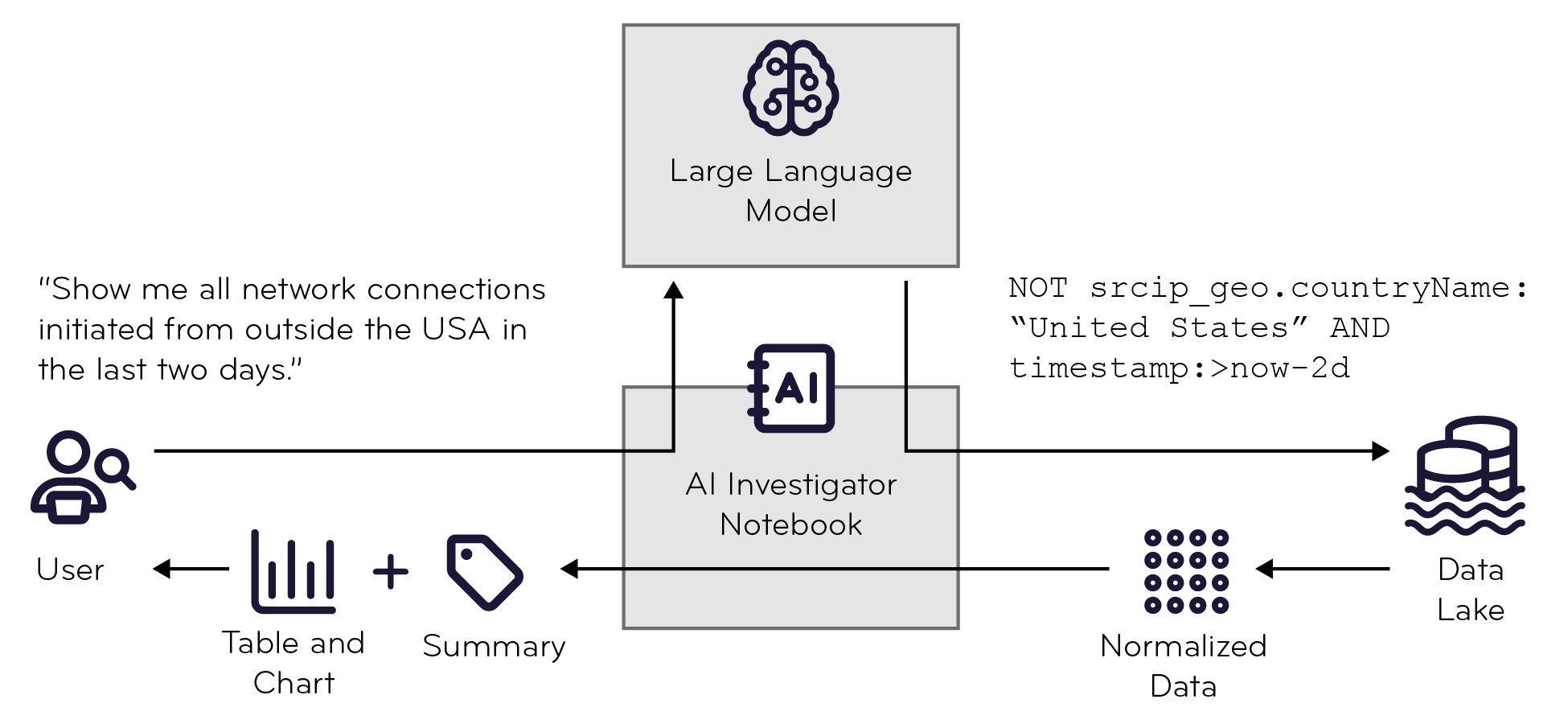
Through AI Investigator, you can leverage artificial intelligence technology to extract, analyze, and investigate the vast number of security records in the Stellar Cyber database. AI Investigator understands prompts entered in natural language and converts them into structured Lucene queries, it provides guidance in investigating and interpreting the results it retrieves. With just a few well-placed questions, you can dig into details on all aspects of your security deployment while shortening the Mean Time to Investigate (MTTI).
When you submit a request (prompt), the security data remains within the platform, ensuring privacy and security, while only the query and data schema are passed to the Large Language Model (LLM) to generate search queries. However, because the query is passed to LLM, compose your prompts in a way that doesn't include any sensitive information or personally identifiable information (PII) that you don't want to pass through AI Investigator to the model.
AI Investigator lets you query data from a variety of sources, such as these:
-
Network traffic logs
-
Windows logs (Sysmon, PowerShell, Windows Defender, and Security-Auditing)
-
Microsoft Entra ID sign-in and risk detection
-
Office 365 audit events
-
Firewall logs
-
EDR alerts from SentinelOne, Sophos, and Trend Micro Vision One
This broad coverage ensures visibility into both on-premises and cloud environments.
Balancing these extensive capabilities, AI Investigator remains tenant-aware, restricting data access to align with user roles and permissions. In short, users have visibility only into data associated with the scope of their user accounts. While root users have visibility into data for all tenants in the entire Stellar Cyber Platform, partners have visibility only into data belonging to tenants in their own tenant groups, and tenant users have visibility only into data for their specific tenant.
The information in the following sections will help you learn how to use AI Investigator to detect and respond to threats effectively:
Check Requirements for On-premises Deployments
Enabling AI Investigator for on-premises deployments typically requires a review by Stellar Cyber Customer Success to ensure your environment meets the necessary requirements. This review includes verifying the availability of Early Access Program functionality and confirming that sufficient memory resources are allocated for the summarization service. Additionally, because the Data Processor must have connectivity to Stellar Cyber AI services, any intervening firewalls must be configured to allow traffic to genai.stellarcyber.cloud. These steps ensure a smooth deployment and operation of AI Investigator.
Ask AI Investigator a Question
Using AI Investigator is as simple as asking it a question and evaluating the results:
-
Log in to the Stellar Cyber UI and select AI Investigator in the main menu bar.
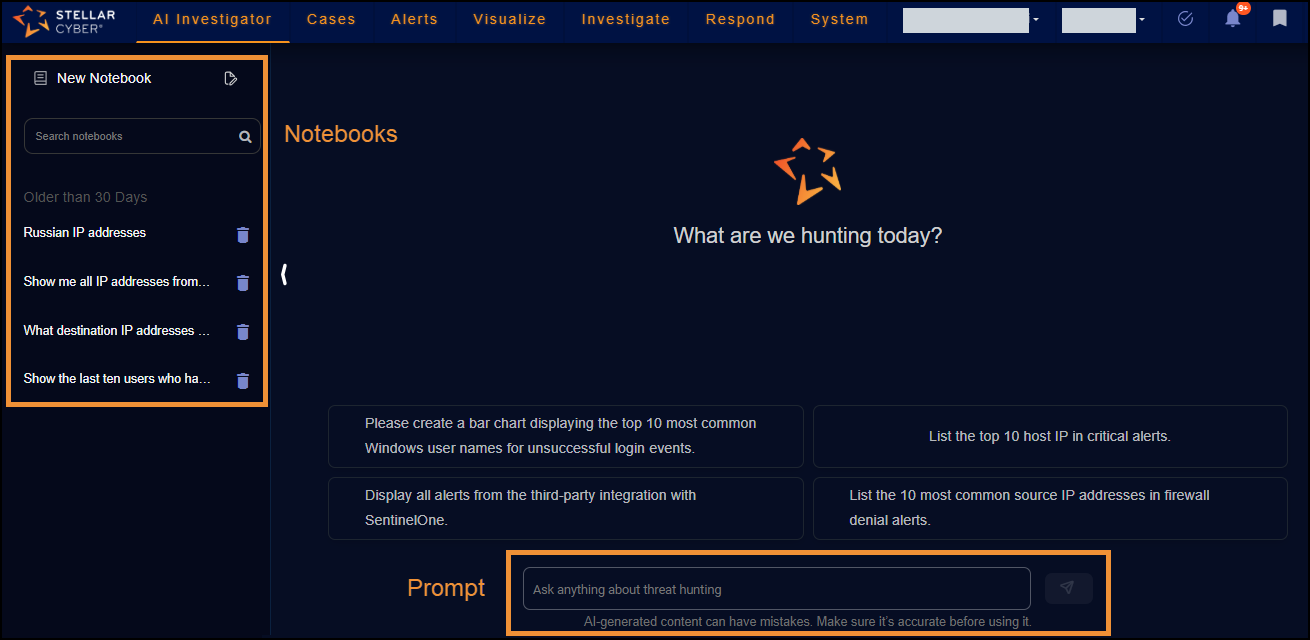
AI Investigator has two main sections: A collapsible left side panel with a set of previously asked questions (referred to as notebooks) grouped by date, and a main section where you enter prompts, which AI Investigator converts into queries, and view results.
The Notebooks panel contains questions you’ve asked in the past. You can search through them or ask the questions again to see fresh results.
The prompt is where you ask your questions.
-
Type a prompt in the text field and press Enter or select the Send message icon to submit it.
Making your prompts more specific elicits better results.
In response, AI Investigator extracts keywords from your prompt and generates a query based on them.
If a generated query includes a single index, the default time range is seven days. If there are two or more generated indices, the default time range is 24 hours so performance is not affected. For the number of indices being queried, you can manually shorten the time range but not lengthen it.
The following table and screen capture show how AI Investigator converts a prompt into a query.
Type of Information in AI Investigator
Example
Description
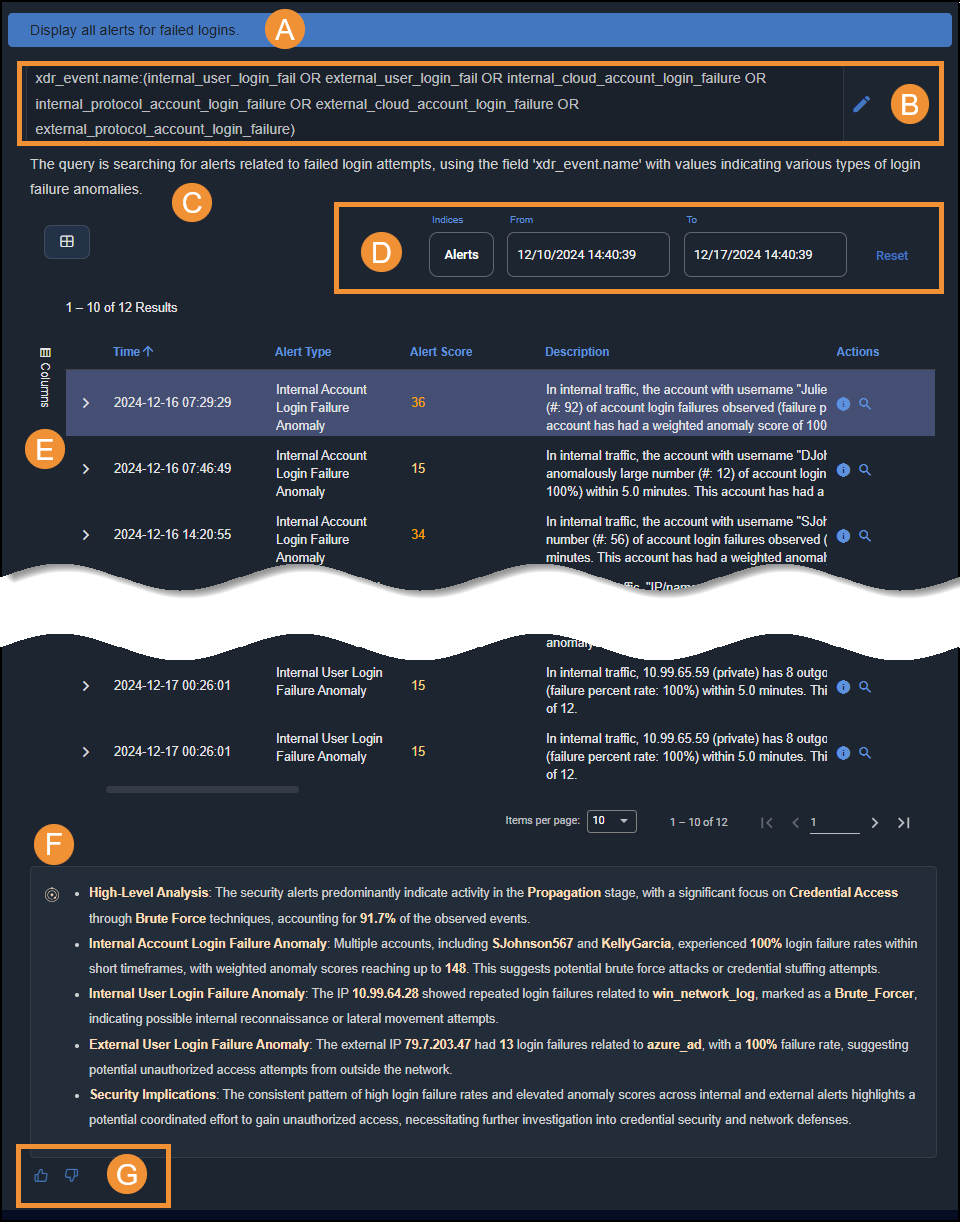
Original prompt Display all alerts for failed logins. After you enter a prompt, it appears at the top of the page. By default, Stellar Cyber creates a notebook and gives it a name derived from the prompt. To change the name, double-select the notebook title and enter your changes. Query conversion xdr_event.name:(internal_user_login_fail OR external_user_login_fail OR internal_cloud_account_login_failure OR internal_protocol_account_login_failure OR external_cloud_account_login_failure OR external_protocol_account_login_failure)This field shows how your prompt was converted into a Stellar Cyber query. You can edit the elements in the query to fine-tune it. Query description The query is searching for alerts related to failed login attempts, using the field
xdr_event.namewith values indicating various types of login failure anomalies.AI Investigator provides a description of how it translated your prompt into a Stellar Cyber query, including the exact fields it used to retrieve the displayed data. Query results (Refer to the screen capture below).
AI Investigator provides an interactive table or chart displaying the results The following screen capture shows the response to a prompt to display all alerts for login failures. Here are explanations of the different components of the response:
-
This is the prompt.
-
This is the query that AI Investigator generates from the prompt. The query is editable.
-
AI Investigator provides a natural language explanation of how it authored the query.
-
Depending on the query, you might be able to adjust parameters for the displayed data. For example, here you can change the indices and adjust the time range.
-
AI Investigator returns results in a table or chart. You can use standard Stellar Cyber table functionality to add or sort columns and navigate through pages of data.
-
AI Investigator provides analysis of its findings for your consideration.
-
Provide feedback on the results. If you select the Thumbs-down icon, additional fields appear so you can supply feedback to Stellar Cyber.
-
-
To add another prompt to the currently active notebook, enter it in the text field at the bottom of the page below the results of your previous question and press Enter to submit it.
Doing so adds the next prompt to your investigation. You can add as many prompts to the same investigation as you want. They're all saved in the notebook whose name is derived from the first prompt you enter.
After entering a prompt, you cannot edit and run it again. However, you can copy a previously entered prompt, paste it, and edit the copy for use as a new prompt.
By default, AI Investigator saves each notebook it generates. You can keep the ones you intend to use again and delete the others. Notebooks also serve as a reference for the types of prompts you used in the past. A search tool lets you look for specific prompts that you've previously created.
-
To start a new investigation—and a new notebook—select New Notebook at the top of the left side panel.
-
To reuse a previous investigation, select an existing notebook, optionally choose a different index or indices to see results from a different index in the database, and set different dates or Reset the dates to see results within a different time range.
Sample Prompts
Here are some sample prompts for AI Investigator to help you get started. Expand each area of interest to explore them.
AI Investigator supports summarizing records only within the aella-ser-*, aella-wineventlog-*, and aella-adr-* indices. It does not process summaries for tables generated by aggregation queries as these already provide a condensed view of data. Similarly, queries related to plotting and visualization are excluded, allowing the summarization feature to focus on event and alert data, where it adds the most value.
-
What users successfully logged in but were flagged for brute force attacks?
-
Which users had their multi-factor authentication (MFA) fail during recent login attempts?
-
What users have logged in successfully using MFA?
-
Show me all Windows password change attempts.
-
What destination IP addresses have been flagged with a bad reputation during recent traffic flows?
-
Which destination IP addresses were associated with known Spyware or Command & Control servers?
-
Which source IP address has transmitted an unusually high amount of outbound traffic?
-
Which destinations are showing anomalous login geolocation deviations between recent login attempts?
-
What destination ports have seen unexpected traffic patterns in the past week?
-
Show me commands that have been executed an unusually large number of times.
-
What systems have seen repeated execution of malicious files with specific MD5 hashes flagged in recent alerts?
-
Which destination IP have been flagged for high-severity alerts?
-
What Windows events indicate system registry changes or unauthorized actions?
-
Which sensors have sent an anomalously high volume of data?
-
Which Microsoft 365 events have been flagged for suspicious activity based on event scores?
-
What cloud resources have been accessed from geographic locations with significant login distance deviations?
-
Which Microsoft Entra ID users are involved in password spray attacks?
-
What Microsoft 365 users have been flagged for unusual volume of file deletion?
-
Which Microsoft Entra ID users have abnormal browsing activities?
-
Which incidents had critical alert scores flagged for immediate attention?
-
What alerts were related to attempts to exploit known vulnerabilities?
-
Which IDS alerts were triggered by multiple signature matches during a single attack?
-
What alerts were triggered by high-fidelity machine learning models?
-
Which security alerts showed user login at an unusual time?
Tips
Chatbot usage: The chatbot is designed for querying and presenting data. Non-data-related topics like greetings or casual questions such as "How's the weather today?" are not supported and will return a standard error message. Focus questions on data analysis.
Follow-up requests: You can ask follow-up questions, but to avoid confusion, use clear transitions like "Add one filter..." or "For the tables above...". This helps the chatbot distinguish between new and follow-up requests.
Be specific: The more precise your request is, the more accurate the response will be. For instance, instead of "Show me all successful logins", write "Show me all successful Windows event logins" to ensure the correct data is retrieved. Mentioning a specific data source typically gets better results, possibly with less latency.
Manage chat length: Because a lengthy chat history might reduce the effectiveness of AI Investigator for that chat, strive to create new chat sessions after discussing a distinct set of issues rather than continuing indefinitely in a single session.
Handling technical issues: If you encounter a technical issue, try asking the same question again.
Keep it simple: For complex requests, start simple and add follow-up questions. This approach minimizes errors and improves response accuracy.
Allow response time: Allow a few seconds for AI Investigator to process each question.
Explicit references in follow-up questions: When asking follow-up questions, always explicitly reference the specific entity (e.g., username, IP address) if it wasn't mentioned in the previous query. Avoid using terms like "this" or "these" to prevent ambiguity because AI Investigator cannot infer these references from earlier responses.
For example:
-
Incorrect: After asking "Show me all failed user login alerts initiated from the IP addresses 192.168.1.15 ", a follow-up such as "Show me the activity of this user" would be unclear because AI Investigator cannot determine which user is being referenced.
-
Correct: Instead, restate the specific entity: "Show me the activity of jsmith@abc[.] com initiated from the IP address 192.168.1.15."
To avoid misunderstandings and get the most accurate results, always provide explicit details when referring to entities in follow-up questions.
Indicate that a follow-up question continues the same topic: When asking a follow-up question, use a connecting phrase to indicate that your next prompt relates to the previous response rather than introducing a new topic. A few examples of connecting phrases:
-
Following up on that...
-
Continuing from that...
-
Based on that, let's add...
In addition, if you include an explicit reference to the AI Investigator's last response or to information in its response, you can strengthen the context of one longer topic in which follow-up questions are a part. Modified examples:
-
Following up on your previous response...
-
Continuing from your last response...
-
Based on the information you just provided, let's add...
Explicitly linking a new prompt with the previous response makes it clear that your aren't introducing a new topic but rather are continuing within the current topic.
Be explicit when providing feedback about queries: If you're not satisfied with the query string that AI Investigator generates when answering a prompt, you can provide feedback in your follow-up prompt. When you do, reference the generated query string in your feedback. A few examples:
-
Regarding the last query string you generated...
-
The previously generated query doesn't fully capture <x>. Adjust it to...
-
Something seems off in the last query you generated. It should be structured like...
Perform an Investigation
The following example demonstrates how an investigation might develop from an initial prompt and response into a chat consisting of a series of follow-up exchanges based on the results of each query.
-
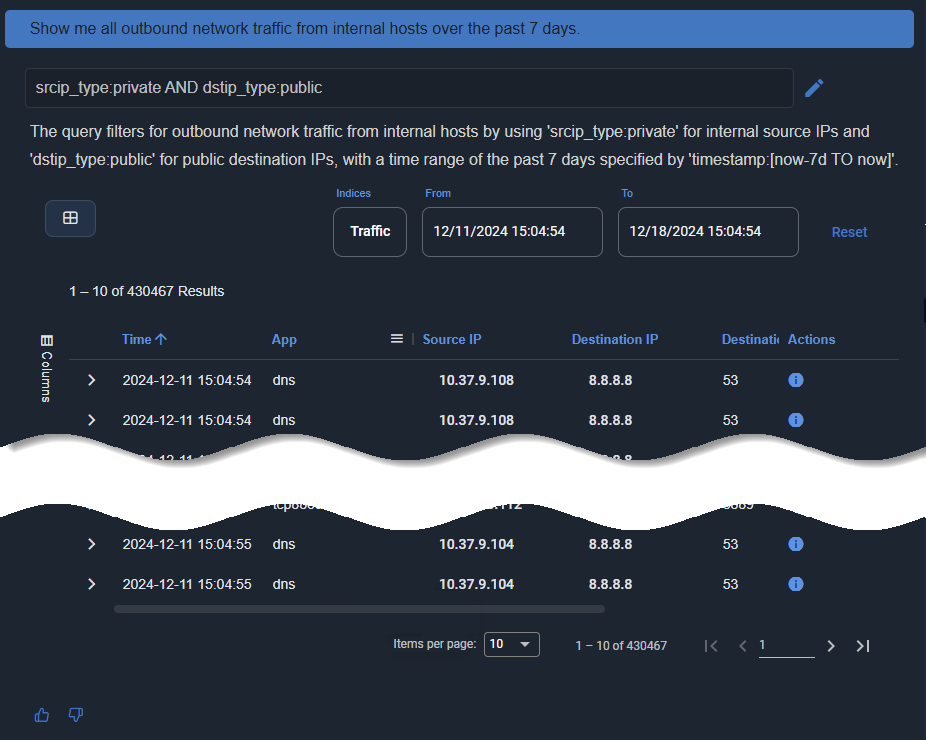
Prompt: Show me all outbound network traffic from internal hosts over the past 7 days.
AI Investigator displays a table showing all outbound traffic sessions over the past 7 days.
-
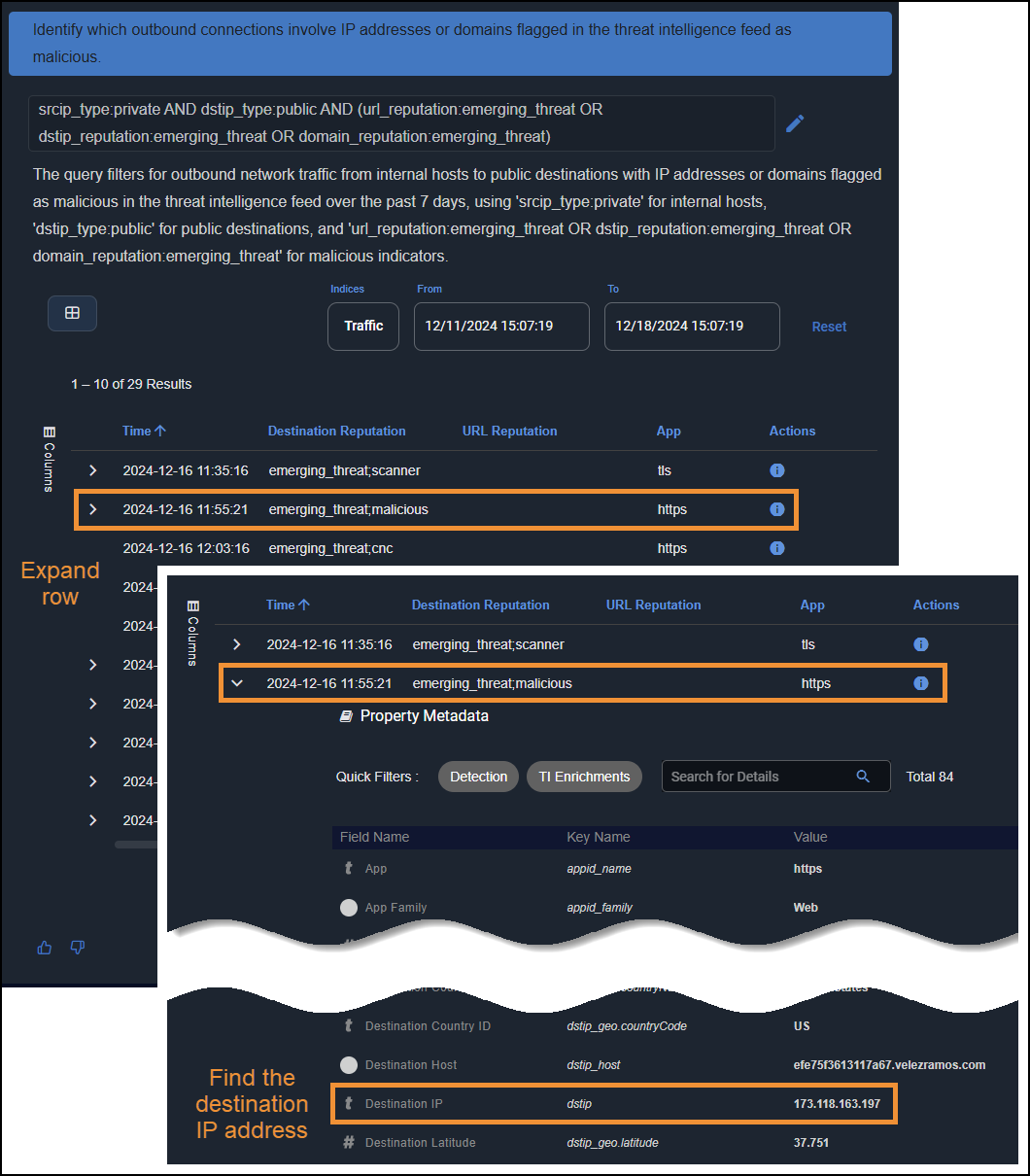
Prompt: Identify which outbound connections involve IP addresses or domains flagged in the threat intelligence feed as malicious.
Use AI Investigator to filter through the outbound traffic sessions and display only those with destinations flagged as malicious. Next you expand rows to find the IP addresses of these malicious destinations, which you then use in subsequent prompts to find which devices initiated the connections.
-
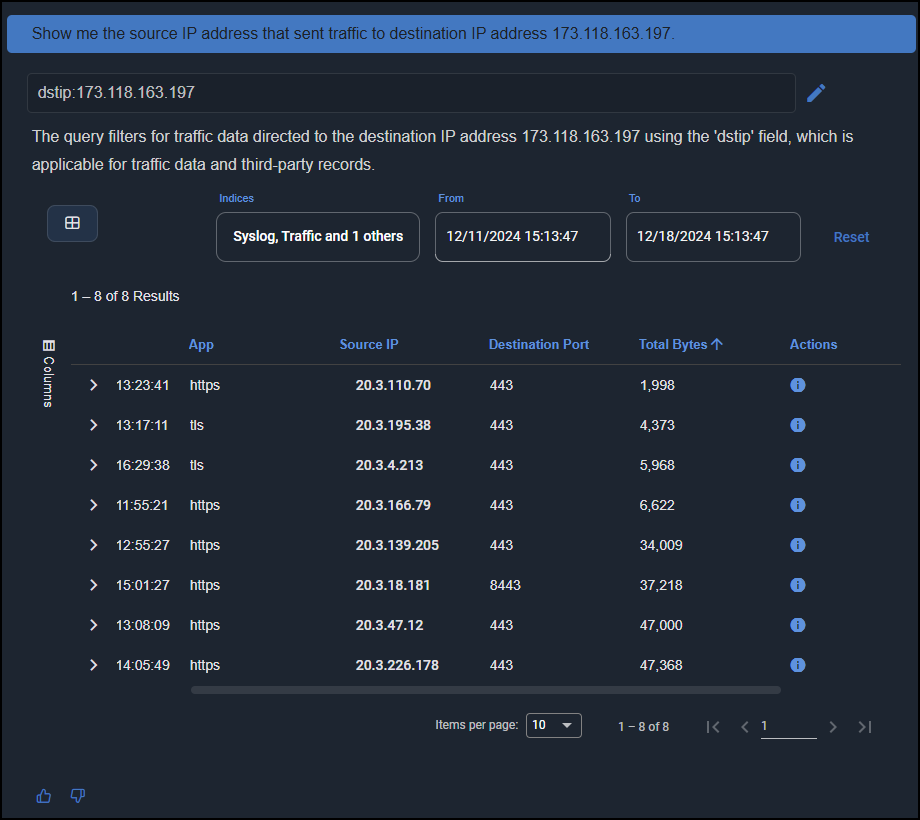
Prompt: Show me the source IP address that sent traffic to destination IP address 173.118.163.197.
AI Investigator displays a table showing all the source IP addresses of devices that connected to the malicious destination in the past 7 days, the application used, destination port, and total number of bytes sent.
You can follow up on hosts that made a suspiciously large number of connections or sent a suspiciously large amount of data.
FAQs
For privacy considerations, see the OpenAI Privacy Policy.
Question: What is the typical query latency in AI Investigator, and why might some queries take longer to process?
Answer: The typical latency for translating and processing a query in AI Investigator is approximately 15 seconds. However, certain types of queries might need additional processing time due to data aggregation on the Stellar Cyber Platform.
Key factors affecting latency
-
Query Complexity: Keywords such as “top” or “rank” often trigger data aggregation tasks; for example, ranking top users or identifying top IP addresses. These tasks involve analyzing and summarizing large datasets, which typically increases processing time.
-
Data Volume: Queries that involve searching across extensive datasets or multiple data sources might take longer due to the volume of information being analyzed.
-
Backend Processing: The Stellar Cyber Platform performs sophisticated data transformations and computations to provide accurate and actionable results, which can contribute to delays for certain requests.
Question: How does AI Investigator use the like/dislike feedback, and why is it important to provide this input?
Answer: The feedback feature in AI Investigator helps improve its performance by identifying areas where responses meet or fall short of expectations. You can provide a thumbs-up (like) for satisfactory responses or a thumbs-down (dislike) when the response doesn’t meet your needs. When you give a thumbs-down, AI Investigator prompts you to specify the reason for your dissatisfaction by selecting options such as “Irrelevant Responses,” “Too Generic,” or “Lack of Context in Summary.”
How feedback is used
-
Improvement of AI accuracy: Each piece of feedback contributes to refining the ability of AI Investigator to understand natural language so it can improve how it processes queries and generates responses.
-
Identifying Weaknesses: Specific reasons for dislikes such as “Inaccurate Information” or “Slow Responses” help the development team pinpoint and address specific shortcomings.
-
Tailoring Future Responses: By understanding common issues, AI Investigator can be optimized to better align with your expectations by improving the relevance, detail, or speed of its responses.
Why it’s helpful to provide feedback
-
Your feedback is essential to fine-tune AI Investigator capabilities, ensuring it evolves to meet your needs more effectively.
-
Detailed feedback helps AI Investigator improve its handling of diverse queries, accommodating different grammatical structures, keywords, and context nuances.
Providing clear, actionable feedback ensures AI Investigator continuously improves so it can offer increasingly more accurate and valuable responses in future interactions.
Question: How does AI Investigator handle telemetry and user prompt data?
Answer: Telemetry and user prompts submitted to AI Investigator undergo a limited anonymization process to protect privacy. This process removes any attribution to the tenant or user who submitted the request. However, the content of the prompt and the resulting search query are not anonymized or tokenized.
Key details
-
Anonymization Scope: AI Investigator removes tenant and user identifiers, so that prompts and queries cannot be directly traced back to an individual or organization.
-
Content Handling: While tenant and user attribution is removed, the actual content of the prompt—that is, the question asked—and the resulting search query remain intact and are stored in their original form.
-
Purpose of Data: This data is securely stored and used solely to improve AI Investigator by refining its natural language processing, enhancing accuracy, and expanding functionality. It is not shared with third parties or used for purposes beyond product improvement.
Stellar Cyber takes privacy and data security seriously and balances these priorities with the need to improve AI Investigator capabilities.