Configuring Modular Sensor Profiles
A modular sensor profile allows you to easily add the features you like to your profiles. This helps simplify your profiles and lets you manage the VM requirements for the sensors based on the modular features they use. As we add new modular features, you can choose to add them to your sensor profiles.
Modular sensor profiles can only be applied to modular sensors. You can:
Keep in mind that VM resource requirements increase as you add more features to the Modular Sensor Profile. Refer to Modular Sensor Specifications for details on the resources required to run different combinations of features in a Modular Sensor Profile, as well as how to use the show module and show module request CLI commands to compare provisioned resources against those required to run specific feature combinations. Stellar Cyber only enables a Modular Sensor Profile on a sensor if the host VM's resources can support it.
Adding a Modular Sensor Profile
Whether you add or edit a modular sensor profile you have the same options, except you cannot edit the profile name. Use the following procedure to add a modular sensor profile:
-
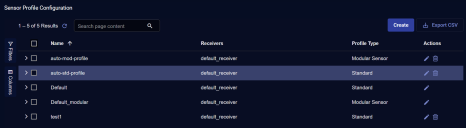
Click System | Collection | Sensor Profiles. The Sensor Profile Configuration page appears, with the Sensor Profiles tab displayed by default.
-
Click Create and select Add Modular Sensor Profile. The ADD SENSOR PROFILE screen appears.
- Enter the Profile Name. We recommend that you establish a naming convention so you can easily understand the intent of each profile by looking at the name. This field can only contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, spaces, and dashes.
-
Choose at least one Receiver. Each sensor profile must have at least one receiver, which is the destination of the data it collects. You can add one receiver of each type: packet and JSON.
See the Receiver configuration page for more information on creating and maintaining receivers.
- Customize the settings for the profile. The available settings are explained below.
- Click Submit. The profile is active immediately .
Keep in mind the following:
-
Log Collector and Log Forwarder are always enabled in Modular Sensor Profiles.
-
The Sandbox and IDS features can only be enabled if Network Traffic is enabled.
Customizing Modular Sensor Profile Features
You can customize these modular sensor profile features:
Log Forwarder
Modular sensor profiles include a log forwarder by default. You can configure:
- Workers
- Data filtering
- Forward to external server

- Compression
- HTTP JSON parser
- Multi-Tenant Log Ingestion
- Raw Log Capture

- Buffering
Log Forwarder Workers
Configure the batch size:
-
Batch Size – Set the record batch size. The default is 100 records. The range is 1-10000.
The sensor batches log records to make transmission more efficient. If your network has high throughput, increase the Batch Size to increase that efficiency.
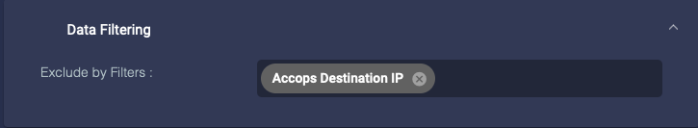
Data Filtering
Add log filters to filter traffic out before sending it to the DP. You can create log filters at System | Collection | Log Filters.
The maximum number of Log Forwarder filters for one sensor profile is 10.
Forward to External Server
You can enable this option to send unparsed logs to an external server, pre-normalization. Logs are still also sent to the DP when this feature is enabled.
Configure external log forwarding as follows:
-
Click Forward to External Server.
-
Enter the IP address or domain name of the external server to which you want to forward unparsed logs.
-
Enter the port.
-
Uncheck Send Metadata if you don't want the sensor to add metadata to the logs forwarded to your external server. If you leave it checked, the sensor adds the log source IP address, ingestion port number, and log source type to the original log in JSON format.
Logs containing non-printing characters, such as Netflow and IPFIX, cannot be forwarded to an external server.
All log lines are truncated to 1024 characters, per RFC 3164.
Compression
Enable Compression for the sensor to compress the parsed logs before sending to the DP. This uses the CPU on the sensor to compress the logs, and the CPU on the DP to decompress. Enable compression to save bandwidth at the expense of CPU on the sensor and DP.
HTTP JSON Parser
Enable the HTTP JSON Parser if you are sending logs via HTTP.
Multi-Tenant Log Ingestion
Enable Multi-Tenant Log Ingestion to allow CEF (Infocyte), Cylance, and selected Stellar JSON parsers to receive logs from multiple tenants. In addition to this setting, the incoming data file must follow specific guidelines described in: Single Sensor Multi-tenant Log Ingestion . Supported parsers are also described in this topic.
Raw Log Capture 
Raw Log Capture can be enabled if you want the sensor to store both raw and processed logs on the DP for built-in parsers. This can be useful in troubleshooting situations when you may want to compare a processed log to its corresponding raw log. Note that the feature only applies to built-in parsers. Custom parsers have their own settings within the parsers themselves.
You can search for raw logs by looking for the parser_raw_msg field in InterFlow records.
Keep in mind that when this feature is enabled, built-in parsers store both raw and processed logs, requiring more storage resources on the DP.
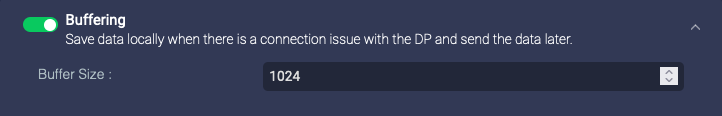
Buffering
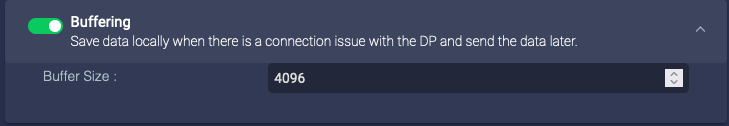
Enable this to enable buffering on the data sensors. If you enable buffering, the data sensor buffers the logs sent to Stellar Cyber. If the logs are received successfully, the sensor deletes the buffered logs. If the buffer is full, the sensor stops buffering logs. The Buffer Size parameter lets you specify the maximum size for all logs buffered:
- Buffer Size—The total logs buffered, in MB
When you disable buffering, any data in the buffer is immediately deleted. Ensure that the sensor has a stable connection to the DP for long enough to transmit all data in the buffer.
Network Traffic
Enable the Network Traffic option to ingest network traffic. When this option is enabled, you can also enable the Sandbox and IDS features. You can configure:
- Application identification
- Application session
- Application metadata
- Process correlation
- Packet deduplication
- Stream slicing
- Handshake failure
- Flood attack
- Buffering
Application Identification
Enable this option for the network sensor to identify applications associated with events.
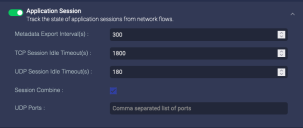
Application Session
Enable this option for the sensor to identify the length of individual network sessions. The parameters specify how often to report the session information and the amount of idle time that can pass before concluding that a session has ended.
If you disable Application Session, network and agent sensors stop sending data to the DP but data sensors continue to process traffic.
If you enable Session Combine, UDP sessions from the specified port to the same destination are combined into a single session.
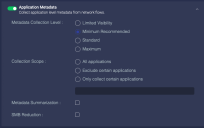
Application Metadata
Enable this to control how application information is collected and which applications are included.
You can disable the collection of application metadata to increase sensor performance and save storage space, but that limits collected data to:
-
Basic session information
-
Packet and byte counts
-
IP address
-
Port
You can set the Metadata Collection Level to Limited Evidence, Minimum, Standard, or Maximum. This controls how many of the information fields are collected.
- 0zz0 login
- 0zz0 password
- activesync login
- aim_express contact_login
- aim_express login
- aims login
- archive login
- archive password
- badongo login
- badongo password
- badoo contact_login
- badoo login
- badoo password
- bebo login
- bebo password
- dhcp agent
- dhcp chaddr
- dhcp ciaddr
- dhcp client_fqdn
- dhcp domain_name
- dhcp dns_server
- dhcp end
- dhcp end_status
- dhcp giaddr
- dhcp host_name
- dhcp inherit_parent
- dhcp ip_lease_time
- dhcp message_type
- dhcp option
- dhcp option_type
- dhcp option_value_buffer
- dhcp request
- dhcp router
- dhcp siaddr
- dhcp sname
- dhcp subnetmask
- dhcp xid
- dhcp yiaddr
- dimp login
- dimp password
- dns dns_entry
- dns dns_query
- dns end
- dns tunneling
- dns flags
- dns host
- dns host_addr
- dns host_addr6
- dns host_type
- dns message_type
- dns name
- dns query
- dns query_type
- dns reply_code
- dns reverse_addr
- dns reverse_addr6
- dns section_type
- dns transaction_id
- dns ttl
- ebuddy contact_login
- ebuddy login
- ebuddy password
- facebook login
- facebook password
- facebook_mail login
- friendster login
- friendster password
- ftp content_type
- ftp data_port
- ftp filename
- ftp filesize
- ftp index
- ftp loadway
- ftp login
- ftp password
- ftp method
- ftp return_code
- ftp transfer_duration
- gmail_basic login
- gmail_chat login
- gmail_mobile login
- gmail_mobile password
- gmx login
- hi5 login
- hi5 password
- http auth_username
- http auth_password
- http code
- http index
- http method
- http proxy_auth
- http proxy_login
- http proxy_realm
- http referer
- http server
- http uri
- http filename
- http file_type
- http forward_addr
- http forward_addr6
- http host
- http mime_type
- http part_content_type
- http user_agent
- ica login_info
- ica login_info_utf16
- icmp code
- icmp message
- icmp rtt
- icmp type
- kakaotalk login
- krb5 error_code
- krb5 login
- krb5 server
- krb5 message_type
- krb5 service
- laposte_webmail login
- ldap hostname
- ldap name
- linkedin login
- live_groups login
- live_hotmail login
- livemail_mobile login
- mailru login
- maktoob login
- mimp login
- mimp password
- msn contact_login
- msn login
- mysql login
- mysql query
- mysql request
- mysql result_set
- mysql sqlstate_code
- mysql number_columns
- mysql number_rows
- mysql query_id
- netflix login
- netlog login
- netlog password
- nfs filename
- nfs filesize
- nfs type_string
- nfs symlink_name
- nfs uid
- niconico_douga login
- nntp login
- nntp password
- odnoklassniki login
- odnoklassniki password
- oovoo login
- orangemail login
- owa login
- paltalk contact_login
- paltalk login
- paltalk_transfer login
- pap login
- pap password
- perfspot login
- perfspot password
- pop3 password
- postgres authentification_type
- postgres error
- postgres login
- postgres password
- postgres query
- postgres query_id
- postgres sqlstate_code
- postgres number_columns
- postgres number_rows
- qq contact_login
- qq login
- qq_transfer login
- radius login_ipv6_host
- radius login
- rambler login
- rambler password
- rambler_webmail rambler_webmail
- rapidshare login
- rapidshare password
- rdp default_username
- rdp username_ascii
- rdp username_raw
- rlogin client_login
- rlogin server_password
- rsh login
- rsh remote_login
- rsync login
- rsync password
- rtmp page_url
- secondlife login
- skyblog login
- skyblog password
- slsk login
- slsk password
- smb login
- smb user_id
- smb nt_status
- smb command_string
- smpp receiver
- smpp sender
- smtp login
- smtp password
- smtp response_code
- snpp login
- snpp password
- socks5 login
- socks5 password
- spdy server_agent
- spdy user_agent
- squirrelmail login
- squirrelmail password
- ssh version
- ssl common_name
- ssl issuer
- ssl subject_alt_name
- ssl validity_not_after
- ssl version
- ssl validity_not_before
- tagged login
- tagged password
- tango login
- tchatche login
- tchatche password
- tds login
- tds password
- tds sqlstate_code
- tds query
- tds query_id
- tds number_columns
- tds number_rows
- teamspeak login
- teamspeak password
- telnet login
- telnet password
- tftp filename
- tftp filesize
- tftp query
- tftp request_filename
- tns login
- tns password
- tns query
- tns sqlstate_code
- twitter login
- twoo login
- twoo password
- ustream login
- ustream password
- viadeo login
- viadeo password
- vkontakte login
- vkontakte password
- winmx login
- yahoo_groups login
- yandex login
- yandex password
- yandex_webmail login
- ymail2 login
- ymail_classic login
- ymail_mobile_new login
- ymail_mobile_new password
- ymsg_conf login
- ymsg contact_login
- ymsg login
- ymsg_transfer login
- ymsg_video login
- ymsg_webmessenger contact_login
- ymsg_webmessenger login
- youtube login
- youtube password
- zimbra login
- zimbra password
- zimbra_standard login
- zimbra_standard password
Minimum collects everything in Limited Evidence. There is currently no difference between Minimum and Limited Evidence.
- amqp class
- amqp type
- amqp method
- amqp replyto
- amqp routing_key
- dhcp circuit_id
- dhcp remote_id
- dhcp remote_id_subtype
- dhcp remote_id_type
- dns web_application_info
- dns ancount
- dns arcount
- dns nscount
- dns opcode
- dns qdcount
- ftp return_content
- ftp offset
- ftp inherit_parent
- ftp data_port_end_offset
- ftp data_port_start_offset
- ftp_data inherit_key
- http cache_control
- http connection_header
- http content_disposition
- http content_encoding
- http content_len
- http cookie
- http date
- http end
- http etag
- http expires
- http image_type
- http is_webdav
- http location
- http ntlm_domain
- http ntlm_user
- http ntlm_workstation
- http part_filename
- http part_header_name
- http part_header_value
- http part_name
- http request
- http request_size
- http server_agent
- http set_cookie
- http smb_client
- http version
- http video_type
- http video_url
- icmp seq
- icmp typeval
- icmp wrong_crc
- krb5 err_cname_name
- krb5 err_sname_name
- krb5 realm
- ldap krb5_enc_data
- ldap krb5_enc_data_type
- ldap krb5_err_cname
- ldap krb5_err_cname_name
- ldap krb5_err_cname_type
- ldap krb5_err_crealm
- ldap krb5_err_data
- ldap krb5_error_code
- ldap krb5_err_realm
- ldap krb5_err_sname
- ldap krb5_err_sname_name
- ldap krb5_err_sname_type
- ldap krb5_err_text
- ldap krb5_kdcoptions
- ldap krb5_message
- ldap krb5_message_type
- ldap krb5_pa_data
- ldap krb5_pa_data_type
- ldap krb5_pa_data_value
- ldap krb5_realm
- ldap krb5_server
- ldap krb5_service
- ldap krb5_ticket
- ldap krb5_ticket_enc_part
- ldap krb5_ticket_name
- ldap krb5_ticket_name_type
- mysql end
- mysql bind_variable
- mysql variable_id
- mysql variable_type
- mysql variable_value
- nfs current_state
- nfs gid
- nfs mode
- nfs procedure
- nfs status
- nfs type
- nfs version
- pop3 attach_filename
- pop3 file_type
- pop3 login_server
- pop3 login
- pop3 received_by_name
- pop3 received_date
- pop3 receiver
- pop3 received_from_name
- pop3 receiver_email
- pop3 sender
- pop3 sender_email
- pop3 subject
- postgres variable_format
- postgres variable_id
- postgres variable_type
- postgres variable_value
- postgres base
- postgres proto_version
- postgres server_version
- rpc message_type
- rpc procedure
- rpc program
- rpc xid
- sip authorization_username
- smb filename
- smb filesize
- smb file_type
- smb directory
- smb domain
- smb file_id
- smb host
- smb krb5_error_code
- smb krb5_err_text
- smb krb5_ticket
- smb loadway
- smb native_os
- smb path
- smtp attach_filename
- smtp attach_size
- smtp file_type
- smtp received_by_name
- smtp received_date
- smtp received_from_name
- smtp receiver
- smtp receiver_email
- smtp sender
- smtp sender_email
- smtp server
- smtp subject
- snmp method
- snmp name
- snmp oid
- snmp value_raw
- snmp version
- spdy location
- spdy mime_type
- ssl certif_sha1
- ssl handshake_type
- ssl organization_name
- ssl parent_common_name
- ssl protocol_version
- ssl server_name
- syslog code
- tds bind_variable
- tds variable_id
- tds variable_type
- tds variable_value
- telnet term_type
- tftp mode
- tns client_hostname
- tns server_hostname
- tns bind_variable
- tns variable_id
- tns variable_type
- tns variable_value
- amqp correlation_id
- amqp exchange_type
- amqp revision
- amqp server_major_version
- amqp server_minor_version
- ica application
- ica application_utf16
- ica priority
- ica service
- mysql base
- pop3 attach_disposition
- pop3 attach_transfer_encoding
- pop3 date
- pop3 received_by_ip
- pop3 received_from_ip
- pop3 received_server_agent
- pop3 received_with
- pop3 receiver_alias
- pop3 receiver_type
- pop3 sender_alias
- pop3 user_agent
- rpc program_version
- rpc state
- rpc version
- sip inherit_key
- sip inherit_parent
- sip method
- sip reply_code
- sip request_call_id
- sip user_agent
- smb attributes
- smb ext_attributes
- smb file_attributes
- smb file_chunk_data_offset
- smb file_chunk_len
- smb krb5_enc_data
- smb krb5_enc_data_type
- smb krb5_err_cname
- smb krb5_err_cname_name
- smb krb5_err_cname_type
- smb krb5_err_crealm
- smb krb5_err_data
- smb krb5_err_realm
- smb krb5_err_sname
- smb krb5_err_sname_name
- smb krb5_err_sname_type
- smb krb5_kdcoptions
- smb krb5_message
- smb krb5_message_type
- smb krb5_pa_data
- smb krb5_pa_data_type
- smb krb5_pa_data_value
- smb krb5_realm
- smb krb5_server
- smb krb5_service
- smb krb5_ticket_enc_part
- smb krb5_ticket_name
- smb krb5_ticket_name_type
- smb search_attributes
- smb search_pattern
- smb security_blob
- smb service
- smb service_data
- smb session_key
- smb share_access
- smtp attach_disposition
- smtp attach_transfer_encoding
- smtp content_language
- smtp content_transfer_encoding
- smtp date
- smtp received_by_ip
- smtp received_from_ip
- smtp received_server_agent
- smtp received_with
- smtp receiver_alias
- smtp receiver_type
- smtp replyto
- smtp sender_alias
- smtp server_agent
- smtp start_time
- smtp stop_time
- smtp user_agent
- tns base
- tns client_os
- tns client_program_name
- tns client_program_path
- tns response_size
- tns server_os
- tns server_port
- tns version
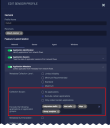
Collection Scope allows you to filter specific metadata that is sent to the Data Processor.
-
Select All applications for no traffic filtering
-
Select Exclude certain applications to collect metadata for all content except the applications and application groups you specify in the selector box. .
-
Select Only collect certain applications to exclude all metadata except that for the applications and application groups you specify in the selector box.
When you select an option other than All applications, the selector box accordingly updates for you to then Exclude or Include the following applications or application groups. Begin typing in the selector box to display a list of configured Application Groups and Applications. Applications Groups are listed first; scroll through the list to get to the set of Applications. When you select an Application Group, the label for it is has a prefix (Group: ) to distinguish it from Applications. In the above image, all the selections are applications except analytics.
In previous releases, Application Groups were referred to as Tags.
Metadata Summarization allows you to reduce traffic to the DP. If you enable this, the sensor groups similar metadata from chatty applications into a single JSON file before sending to the DP.
Finally, you can enable SMB Reduction to reduce the amount of metadata collected for SMB commands. This is especially helpful in increasing your compression ratio if your network has a great deal of SMB traffic. If you enable this, metadata is only collected for:
- session setup
- logoff
- read
- write
Process Correlation

Enable this to build correlations between processes running on the sensor and host, and the IP address/port visible in traffic. The processes monitored include:
- log forwarder
- IDS
- maltrace
- aella_flow
- SSHD
- HTTP
You can set the sampling time interval.
Packet Deduplication
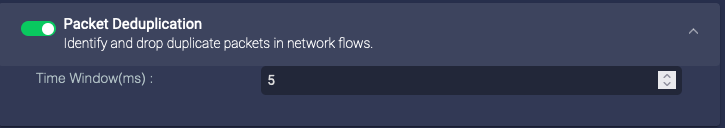
Enable this for the sensor to perform packet deduplication. This reduces storage by removing duplicate data. However, it uses processing power on the sensor to analyze the data and can significantly slow system performance. When this option is enabled, you can also set the deduplication time window.
Enable with caution.
If you have no need for deduplication (for example, if you have a sensor for every network segment), disable it.
Stream Slicing
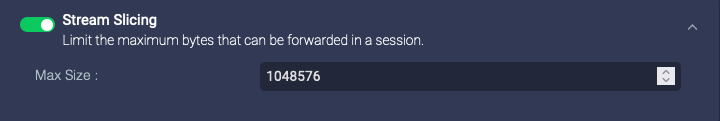
Enable this to perform stream slicing, which truncates sessions at the specified length. This can reduce the bandwidth used.
This has no effect if you use local file assembly.
Handshake Failure
Enable this to detect handshake failures and allocate resources for that effort:
- Time(s)—amount of time the sensor collects failures to get to the threshold
- Threshold—the number of failures over the specified time before this detection is triggered
- Report Interval(s)—interval between reports to the DP if there are multiple failures
- Memory Limit (%)—maximum percentage of memory used by
aella_flowfor this detection
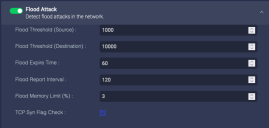
Flood Attack
Enable this to report flood attacks:
- Flood Threshold (Source)—the number of new session requests per second from a single source before an attack is reported
- Flood Threshold (Destination)—the number of new session requests per second from any source before an attack is reported
- Flood Expire Time(s)—the number of seconds without new session requests after which we stop considering it an attack, and the sensor sends a
session_endmessage to the DP - Flood Report Interval(s)—during an attack, the interval at which the sensor reports the attack to the DP (so that the DP isn't flooded with reports of the flood attack)
- TCP Syn Flag Check—only counts session requests if the SYN flag in the packet is set
Buffering
If you enable buffering, the sensor buffers the data sent to Stellar Cyber. If the buffered data is received successfully, the sensor deletes the buffered data. If the buffer is full, the sensor stops buffering. The Buffer Size specifies the maximum amount of data buffered.
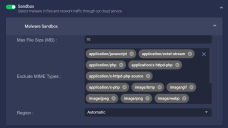
Sandbox
Enable the cloud sandbox to detect malware in network traffic. You must enable Network Traffic to enable the sandbox.
You can control the type and maximum size of scanned files, as well as the region of the sandbox used:
- Max File Size (MB)—The largest file that will be scanned. The default and maximum values are both 10 MB.
- Exclude MIME Types—Which file types are scanned. By default all known file types are scanned. Add the file types you'd like to exclude from scanning.
- Region – Secifies the geographical region of the malware sandbox used by this profile. By default, this option is set to Automatic and the sensor selects the sandbox with the lowest latency relative to its own location. You can optionally override the Automatic option and choose a sandbox in a specific geographic location from the dropdown.

Note: This feature is new in the 4.3.5 release. Sensors upgraded from previous releases all use the Automatic option by default until a new profile with a different setting for the Region option is applied.
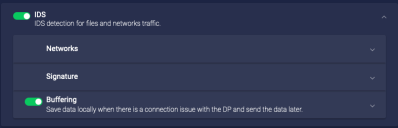
IDS
Enable IDS to detect malicious activity in network traffic. You must enable Network Traffic to enable IDS.
You can configure:
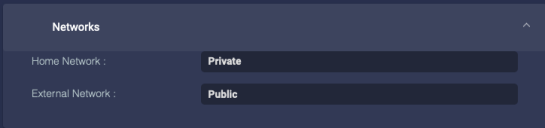
Networks
Choose the Home Network. If you choose Specific, you can enter the IP address range.
Choose the External Network. If you choose Specific, you can enter the IP address range.
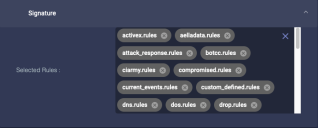
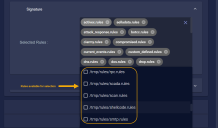
Signature
Choose the rule sets to use. These rules are integrated by Stellar Cyber from third-party threat intelligence. You can choose which rule sets to use, but you cannot add your own rules.
Stellar Cyber regularly pushes new rule sets so that they are available for selection in a sensor profile. Click at the bottom of the Selected Rules list to see a dropdown of the rules available for selection. For example:
Buffering
If you enable buffering, the sensor buffers the data sent to Stellar Cyber. If the buffered data is received successfully, the sensor deletes the buffered data. If the buffer is full, the sensor stops buffering. The Buffer Size sets the maximum amount of data buffered.
Aggregator 

Enable this for the sensor to act as a data aggregator for other sensors.
If you enable the aggregator for this modular sensor, you cannot configure this sensor to use another aggregator.
The modular aggregator forwards aggregated traffic to the DP configured on the modular sensor. It also uses the receivers configured for the modular sensor, so you don't have to configure an aggregator profile.
As soon as you submit the modular sensor profile, you can configure sensors to use the modular aggregator as you would a dedicated data aggregator.
Only Windows Server Sensors can forward traffic to an aggregator in the 5.0.2 release.
Starting with the 5.0.4 release, Linux server sensors can forward to an aggregator, too. However, the feature can only be enabled from the Linux server sensor's CLI (set/show aggregator).
Keep in mind that TCP Port 8080 must be open between the sensor and the aggregator for successful communications.
Tenable Nessus 
This feature is supported on modular sensors running v4.3.4 or later. Stellar Cyber recommends that you provision the modular sensor with an additional 1.5 GB of RAM and 1 vCPU when you enable this option.
Enable this feature to install a tenable nessus vulnerability scanner on your Stellar Cyber modular sensor, and link it to your nessus tenable.io account. After you have linked the scanner instance, you can initiate and monitor scans from the tenable.io
-
Click System | Collection | Sensor Profiles. The Sensor Profile Configuration page appears, with the Sensor Profiles tab displayed by default.
-
Click Create and select Add Modular Sensor Profile. The ADD SENSOR PROFILE screen appears.
-
Log into your tenable.io account as an administrative user (https://cloud.tenable.com).
-
Navigate to Settings > Sensors
-
From the Nessus Scanners tab, select the sub-tab for Linked scanners.
-
Click the link to Add Nessus scanner.
-
From the dialog that displays, copy the Linking Key and save it to a file.
-
Return to the Stellar Cyber console, Modular Sensor profile you are adding or editing.
-
Locate the section labeled Tenable Nessus, and toggle the feature on.
-
In the panel that displays, enter the Linking Key.
-
If needed, modify the default settings for Host and Port.
-
Click Submit.
After this profile is associated with a sensor, you can select that sensor IP address when you create or edit a scan in the Vulnerability Management > Scans panel.