Creating New Alert Types
In addition to the alert types provided by Stellar Cyber, you can create your own custom alert types. You create alerts using an automated threat hunting playbook. The alert, when triggered, then appears in the UI with the existing alerts.
The steps below are an abbreviated sequence of creating a custom alert. To edit the alerts you create, access the Respond | Automation page.
For a detailed description of each section in the Automated Threat Hunting panel, refer to Adding or Editing a Playbook.
-
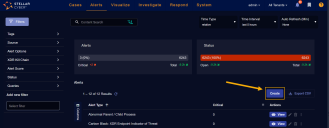
Display the Stellar Cyber Alerts page.
-
Click the Create button.
-
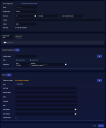
The playbook page is displayed.
This page offers the following sections you can use to create your alert:
-
Alerts: Specify the basic parameters for your alert type, including a name, a schedule, and so on.
-
Queries: Specify whether you want to use a pre-existing query as a basis for your alert, create new one. Details for working with the Query Builder using this pane are described in Using Queries and the Query Builder.
-
Correlation: Build a correlation, if you specified in the Query block above.
-
Condition: Specify the conditions for which the alert should be triggered.
-
Actions: Specify the XDR Kill Chain parameters and other final details for your alert type.
-
-
The top pane, Alert Configuration, allows you to set up parameters for how to run the alert type you are creating.
-
Optionally load settings from a pre-defined template.
-
Enter a Name for the alert.
-
The remaining parameters in this pane have default values you can override. Ideally, select which tenant or tenant group this applies to, which Index the alert should be based on, and the type of alert (Query or Correlation).
-
-
Use the Queries pane to select an existing query as the foundation of your alert type, optionally modify it, or create a new one using Stellar Cyber's Query Builder. If desired, you can toggle Calculations to further tune how your alert should handle certain fields. An example of using calculations is shown in ATH Example: Half-Opened Sessions
-
From the Condition Configuration pane, you must specify one or more conditions to trigger the alert. This is required in order to populate the next pane. Field details are described in the Standard Metadata Dictionary
-
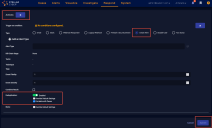
From the Actions pane, you specify the final parameters for your alert type.
Alert types created in previous Stellar Cyber releases may contain deprecated labels. If you loaded from a pre-defined template, a warning may display to report that the fields for Event Type and Event Category need to be updated. If that warning displays, update the fields for XDR Kill Chain, Tactic, and Technique, OR enter a value in the Tag field.
-
Select which condition should trigger the alert type.
-
The Action Type is pre-set to Create Alert when you launch this configuration page from within a Detect page. (When you configure Threat Hunting Automations, the same overall playbook page is displayed, but you are offered more Action Types for your automation.)
-
Enter a name for the new alert type.
-
Select the Kill Chain Stage, Tactic and Technique. These three fields are inter-dependent. Stellar Cyber flags these three fields when one contains an incompatible entry. For details on the stages and relationships of these fields, refer to Understanding the XDR Kill Chain.
-
Specify the desired Fidelity and Severity score associated with this alert.
-
- Click Submit.
The playbook runs immediately, and the new alert type appears.
For details on these settings, see the Automated Threat Hunting article.
About Correlating Alerts with Cases
The raw type of Automated Threat Hunting (ATH) custom alerts can be correlated with cases. A custom alert type is raw if there is no aggregation or correlation.
In addition, the following built-in correlation alert types use ATH correlation rules for detection and are correlated with cases:
-
Exploited C&C Connection
-
External/Internal Exploited Vulnerability
Alerts are correlated with cases if the Correlate with Cases checkbox is selected. The resulting deduplicated alerts are included in cases.
To correlate alerts with cases: