Rule-Based Alert Type Details
Rule-based detection detects anomalies by observing events in the system and applying a set of rules that lead to a decision.
Certain Stellar Cyber alert types are based on specific rules. This topic describes information relating to rule-based alert types as well as some differences between rule-based and built-in alert types.
Rule-Based Alerts Kill Chain Mapping
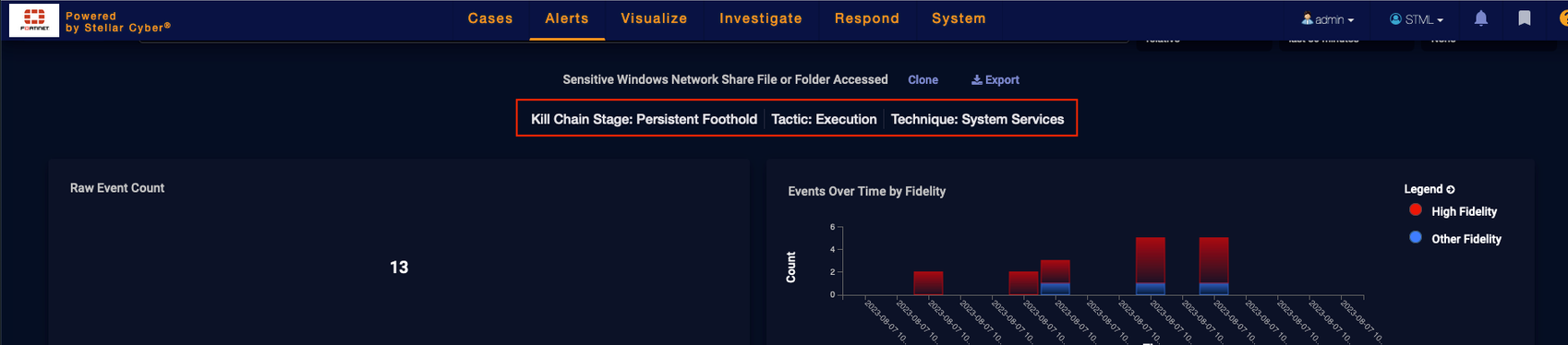
Rule-based alerts have general kill chain mapping information such as Stage, Tactic, and Technique, as follows:
Based on what the rule detects, each rule can have a different Stage, Tactic, and Technique, as follows:
Getting Rule-Based Alerts Details
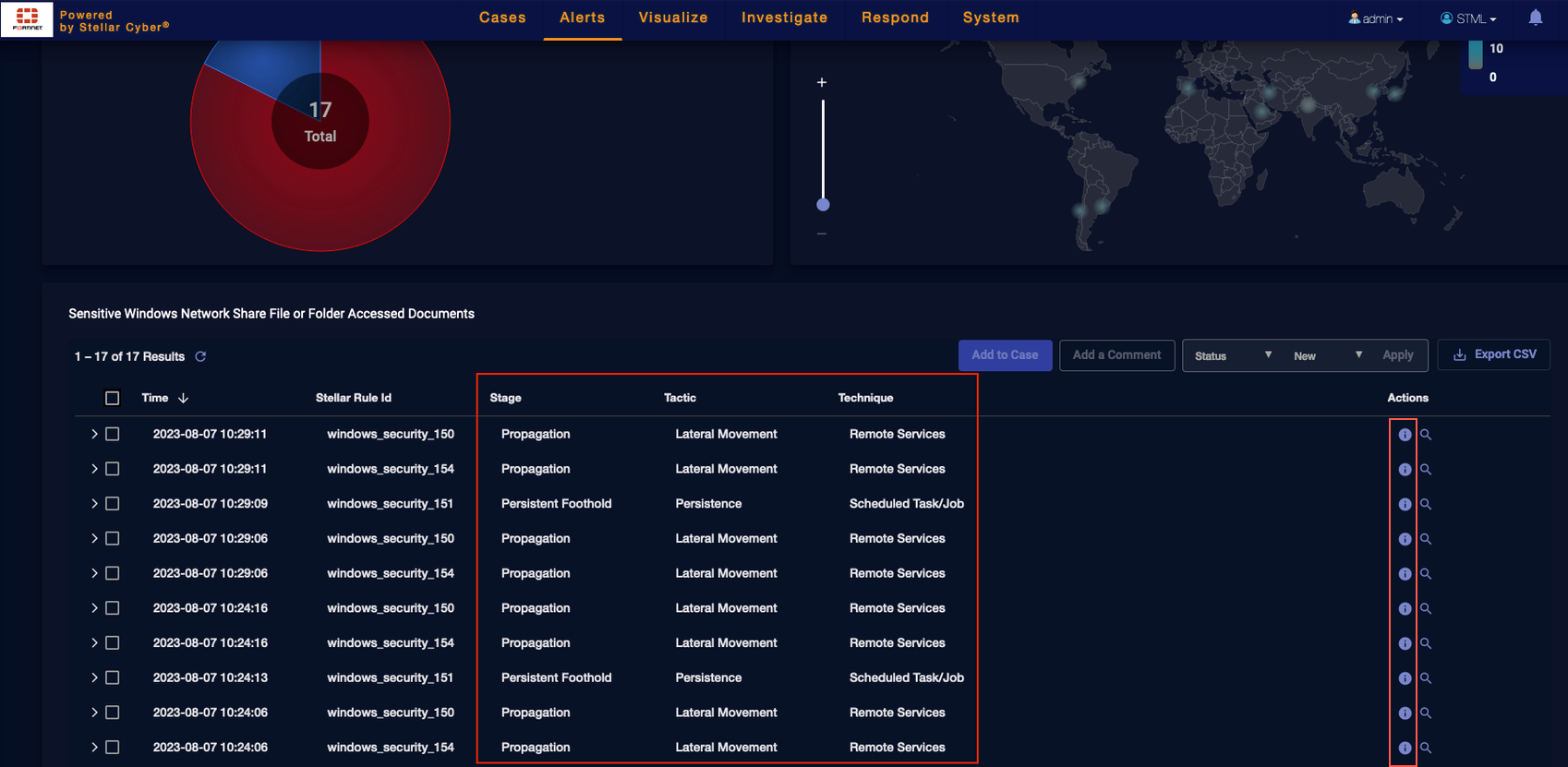
In the Actions column of the table, click i or More Info to display details on an individual rule-based alert.
To get the Knowledge Base description for an individual rule-based alert, in the Key Fields tab, click the Stellar Rule ID link, for example, windows_security_154.
For links to the Knowledge Base description for all rule-based alert types, see Rule-Based Alert Types.
Rule Matching in Queries
Rule matching in queries includes both case-sensitive matching and case-insensitive matching. Whether to use case-sensitive or case-insensitive matching depends on the rule as well as the relevant fields specified in the rule.
For example, case-sensitive matching means using the exact query string. For example, if get is expected, Stellar Cyber will not trigger an alert for Get or GET.
For case-insensitive matching, Stellar Cyber will trigger an alert for get, Get, and GET.
In general, rule matching is case-sensitive, but there are exceptions. For the following rules and fields, case-insensitive matching is being used on:
-
Suspicious PowerShell Script:
event_data.ScriptBlockText -
Suspicious Process Creation Commandline (currently Windows only):
event_data.CommandLineandevent_data.ParentCommandLine -
Suspicious Windows Network Connection:
event_data.Image -
Suspicious LSASS Process Access:
event_data.CallTraceandevent_data.TargetImageandevent_data.SourceImage -
Abnormal Parent / Child Process:
parent_proc_nameandprocess_name -
Miscellaneous IDS rules:
ids.signature
Windows Rule-Based Alerts
Windows rule-based alerts require the updated Windows Detection Profile (Low Volume) in the sensor profile settings.
Metadata for Rule-Based Alerts
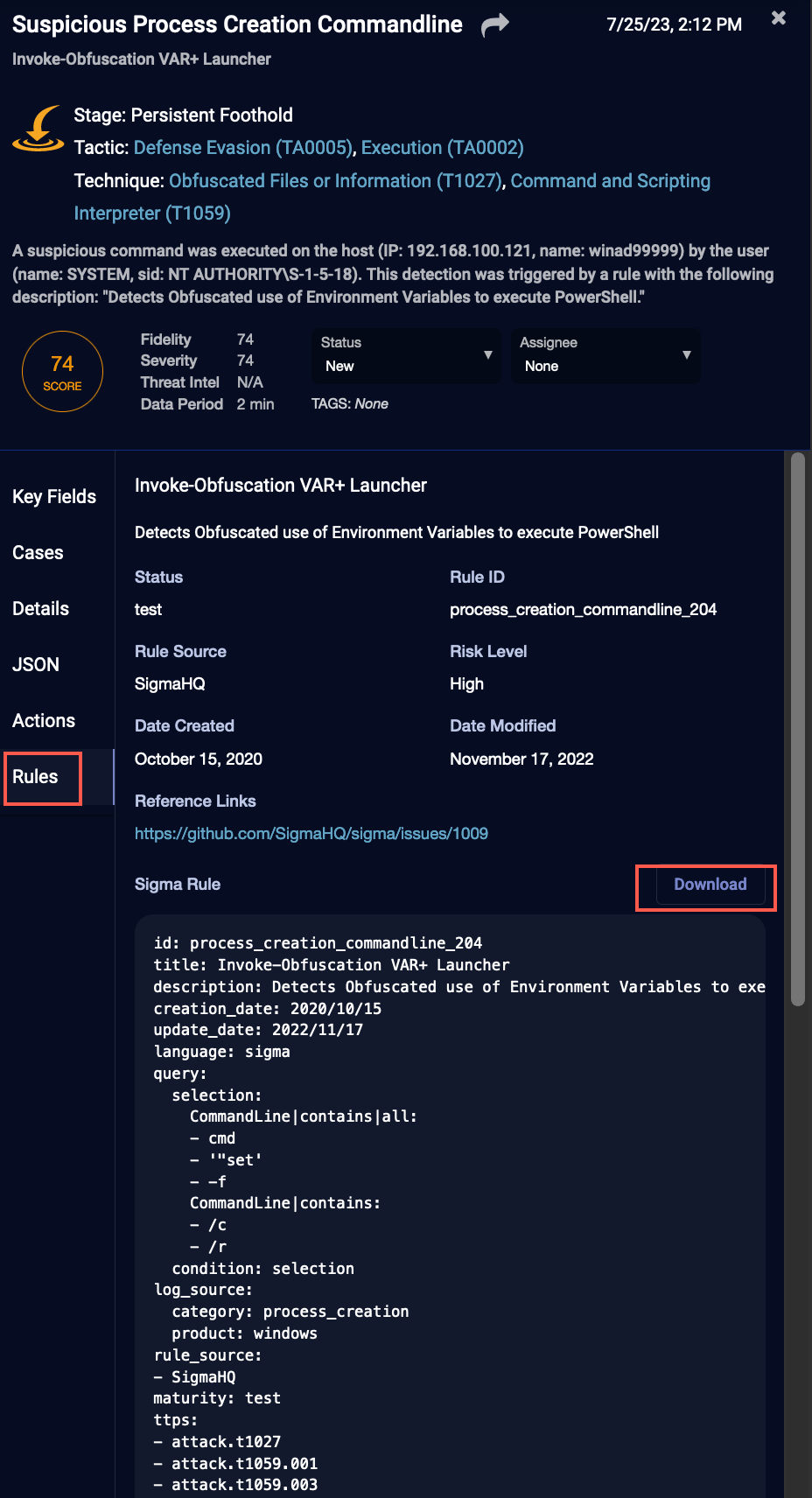
For alert types from rule-based detection, the Rules tab displays the rule's metadata.
The Rules tab displays metadata about the rule itself, such as the name of the rule, description, status, rule ID, and other fields. It also displays the rule configuration in YAML format, which you can download.
Maturity Status
In the YAML format in the Rules tab, there is a maturity status, for example, maturity: test. Stellar Cyber passes any status from Sigma or other open source rule sources. It also develops rules internally.
The following are the maturity statuses for both Sigma and non-Sigma rules:
-
Production—for rules that are reliable in a production environment
-
Stable—for rules that have had one year of use
-
Test—for rules that have had months of use
-
Experimental—for new rules
The status of a rule may be updated in the future based on observations made.
Number of Rule-Based Alerts

The number of rule-based alerts of each type are as follows:
| Rule-Based Alert Types | # of Rules |
|---|---|
| PowerShell Script | 127 |
| Process Creation Commandline | 229 |
| Process Creation Parent/Child | 67 |
| AWS | 96 |
| Microsoft Entra (formerly Azure AD) | 72 |
| DNS | 2 |
|
Windows, including:
|
151 |
| Total | 744 |
For links to the Knowledge Base description for all rule-based alert types, see Rule-Based Alert Types.