Installing a Modular Sensor in Azure
This topic describes how to install a Modular Sensor in a Microsoft Azure environment. Refer to the following sections for details:
- About Modular Sensors
- Site Preparation
- Authorizing the Stellar Cyber Software Images
- Applying a Token to the Installed Sensor
- Configuring a Static IP Address (Optional)
Use our example as a guideline, as you might be using a different software version.
Stellar Cyber does not support the installation of third-party software on its virtual or physical device sensors.
About Modular Sensors
Sensors provide the data gathering foundation for Stellar Cyber's OpenXDR platform, gathering the right data with context. Modular sensors are purpose-built Stellar Cyber sensors that include both the host and the Stellar Cyber monitoring software. They are provided as both physical devices (Photon sensors) and virtual machine images for different target environments.
Previous releases provided a variety of different types of device sensors, including Network, Security, and Modular. Going forward, the only type of device sensor is Modular. You can use the Modular Sensor Profile to enable whatever sensor features you like, creating the same functionality provided by the different sensor types in previous releases.
A modular sensor lets you easily add the features you like to your sensor. This helps simplify your deployment and lets you manage the VM requirements for the sensors based on the modular features they use.
Modular Sensors always include log ingestion. From there, you can enable different features as part of your modular sensor profile:
-
Enable the Network Traffic feature to monitor the virtual environment, the physical environment if connected to the span port of a physical switch, or the LAN segment via a mirror port on a switch. The sensor monitors network and server response times and can identify applications.
The sensor converts that information to metadata and forwards it to the DP as Interflow. The DP can then provide security, DDoS, and breach attempt detections.
-
Enable the Sandbox and IDS features to improve your security posture:
- Sandbox lets you detect malware in files and network traffic through Stellar Cyber's integrated cloud service and also provides anti-virus services.
- IDS lets you detect intrusion attempts using both files and network traffic.
Keep in mind that VM resource requirements increase as you add more features to the Modular Sensor Profile. Refer to Modular Sensor Specifications for details on the resources required to run different combinations of features in a Modular Sensor Profile, as well as how to use the show module and show module request CLI commands to compare provisioned resources against those required to run specific feature combinations. Stellar Cyber only enables a Modular Sensor Profile on a sensor if the host VM's resources can support it.
Site Preparation
Click to see the minimum system requirements for installing a modular sensor. Then, select an Azure instance type that meets the stated requirements for your expected sensor workload.
The Azure instance types in the az create commands in the procedure below use the instance types listed below:
Keep in mind that these are example instance types that meet the requirements stated in Virtual Appliance Sizing Specifications. You can select other instance types with the necessary vCPUs and RAM to perform your expected workload, as stated in the system requirements.
- Modular Sensor – Standard_B12ms
To prepare for the installation:
-
Open firewall ports for log ingestion.
-
Open firewall ports for the features you plan on enabling in the Modular Sensor Profile for this sensor.
-
Contact Stellar Cyber support (support@stellarcyber.ai) to have the SaaS Modular sensor image for Azure deployed in your region. You will need to provide the Azure region for the sensors your are installing.
Do this at least a day before installing, so we have enough time to deploy the images to your region.
Authorizing the Stellar Cyber Software Images
You must authorize the Stellar Cyber software images so that they are available in the Azure portal:
Use our example as a guideline, as you might be using a different software version.
-
Log in to your Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com/. The Dashboard appears.
-
Click Azure Active Directory. The Overview appears.
-
Click Properties.
The Properties page appears.
-
You need the Tenant ID both in the following step and later in the procedure.
-
Put your Tenant ID in the following URL and paste it in your browser:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant id>/oauth2/authorize?client_id=58238038-43b4-4446-8260-0fa97ace1085&response_type=code&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.microsoft.com%2F
The Permissions requested message appears.
-
Click Consent on behalf of your organization.
-
Click Accept.
-
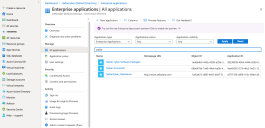
Click Enterprise Applications.
The Enterprise applications | All applications page appears.
-
Search for Stellar. The Stellar Cyber applications that you authorized appear.
If you don't see any Stellar Cyber applications, contact Stellar Cyber support.
-
You can either create a new Resource Group for the deployment or deploy into an existing group. Use this step to create a new Resource Group. Otherwise, you can skip to the next step.
-
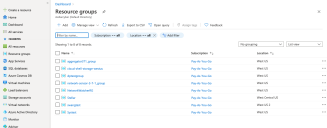
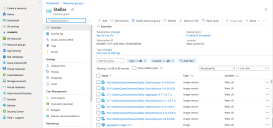
Click Resource Groups.
The Resource groups page appears.
-
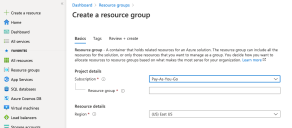
Click Add. The Create a resource group page appears.
-
Choose your Subscription.
-
Enter the name of your group in the Resource group field.
-
Choose the Region where you want to deploy the resource.
-
Click Review create.
-
Click Create. The resource group is created and the Resource groups page appears.
-
-
Click the name of the resource group where you want to deploy the sensor. This is either the resource group you just created or an existing resource group.
The group details appear.
-
Click Access control (IAM).
The Access control (IAM) page appears.
-
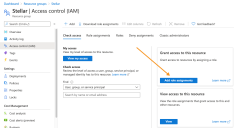
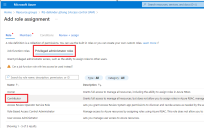
Click Add role assignments to display the Add role assignment controls.
-
Click on Privileged administrator roles and choose the Contributor option, as illustrated below:
-
Leave the default selection of User, group, or service principal in the Assign access to drop-down.
-
Enter Stellar in the Select field. The available Stellar Cyber software packages appear.
-
Choose Stellar Cyber Software Packages.
-
Click Save. The Resource groups page appears again.
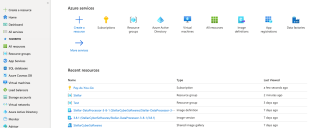
-
Click Home. The Azure services page appears.
-
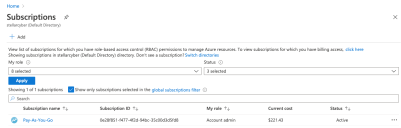
Click Subscriptions. The Subscriptions page appears.
-
Choose your subscription. The subscription details appear.
-
Click Resource providers.
The Resource providers page appears.
-
Select Microsoft.Network.
-
Click Register.
-
Select Microsoft.Compute.
-
Click Register.
-
Click Cloud Shell.
A PowerShell windows opens and connects.
-
Enter the following 3 commands to get an access token from the Stellar Cyber Azure portal:
az account clear
az login --service-principal -u '58238038-43b4-4446-8260-0fa97ace1085' -p '3238Q~KMtVAIyuC6gDVMhboKEW7w6W~bXYQhFcZx' --tenant '2f580e30-1cc1-4c08-9e80-704999508e1a'
az account get-access-token
-
Enter the following commands to get the access token from your tenant ID. Replace Tenant ID with the value you copied earlier.
Make sure you use your Tenant ID, copied from your Azure Portal, as described in this step.
az login --service-principal -u '58238038-43b4-4446-8260-0fa97ace1085' -p '3238Q~KMtVAIyuC6gDVMhboKEW7w6W~bXYQhFcZx' --tenant '<Tenant ID>'
az account get-access-token
-
If you have multiple Azure subscriptions, use the
az account list --output tablecommand to make sure that the subscription where you want to deploy the sensor is currently the default. For example:CopyPS /home/j> az account list --output table
Name CloudName SubscriptionId State IsDefault
Pay-As-You-Go AzureCloud xxxxxxxx-f477-4f2d-94bc-35c00d3d5fd8 Enabled False
Subscription-Dev AzureCloud xxxxxxxx-ac50-4d82-a6ea-a14db86f3957 Enabled True
Subscription-QA AzureCloud xxxxxxxx-9114-4cb0-a044-7e01f074575c Enabled FalseIn this example, Subscription-Dev has IsDefault set to True and is where the deployment will take place. You can change the default subscription with the
az account set --subscription <subscription>command. Let's change the default subscription to Subscription-QA:CopyPS /home/j> az account set --subscription xxxxxxxx-9114-4cb0-a044-7e01f074575c
PS /home/j> az account list --output table
Name CloudName SubscriptionId State IsDefault
Pay-As-You-Go AzureCloud xxxxxxxx-f477-4f2d-94bc-35c00d3d5fd8 Enabled False
Subscription-Dev AzureCloud xxxxxxxx-ac50-4d82-a6ea-a14db86f3957 Enabled False
Subscription-QA AzureCloud xxxxxxxx-9114-4cb0-a044-7e01f074575c Enabled TrueAfter changing the default subscription, the sensor will now be deployed in Subscription-QA.
-
Create a Modular Sensor VM.
Keep in mind that these commands use example instance types that meet the system requirements, including SSD storage. You can specify a different instance type with sufficient vCPUs and RAM to handle your expected workload while making sure to observe all system requirements.
Note that any resources you specify in the
az vm createcommand must already exist in the same resource group where you are creating the VM. This includes any values you supply for theresource-group,vnet-name,subnet,subnet-address-prefix, andnsgarguments.You can also use variables to pass values for the parameters in the
az vm createcommand. Refer to Using Shell Variables to Create the Sensor VM for details.Enter the following command to create a modular sensor VM. Replace <resource-group> with an existing resource group in your deployment and <version> with the version of software you want to install (for example, 5.2.0):
az vm create --size Standard_B12ms --resource-group <resource-group> --name StellarModularSensor --image "/subscriptions/0e28f851-f477-4f2d-94bc-35c00d3d5fd8/resourceGroups/Stellar/providers/Microsoft.Compute/galleries/StellarCyberSoftwares/images/Stellar-ModularSensor/versions/<version>" --admin-username azureuser --admin-password P@ssw0rd#2022 --storage-sku StandardSSD_LRS --os-disk-size-gb 128Note that you can optionally specify the virtual network, subnet, and network security group to be used by the VM by including the
--vnet-name,--subnet, and--nsgarguments. The resources you specify must exist in the same resource group where you are creating the VM. For example, for a modular sensor:az vm create --size Standard_B12ms --resource-group <resource-group> --name StellarModularSensor --nsg <network-security-group> --vnet-name <vnet-name> --subnet <subnet-name> --subnet-address-prefix <subnet-cidr> --image "/subscriptions/0e28f851-f477-4f2d-94bc-35c00d3d5fd8/resourceGroups/Stellar/providers/Microsoft.Compute/galleries/StellarCyberSoftwares/images/Stellar-ModularSensor/versions/<version>" --admin-username azureuser --admin-password P@ssw0rd#2022 --storage-sku StandardSSD_LRS --os-disk-size-gb 128You can also install the sensor without a public IP address by including the
--public-ip address ""argument. For example, here's the same command from above with the--public-ip address ""argument included:az vm create --size Standard_B12ms --resource-group <resource-group> --name StellarModularSensor --nsg <network-security-group> --vnet-name <vnet-name> --subnet <subnet-name> --subnet-address-prefix <subnet-cidr>--public-ip address "" --image "/subscriptions/0e28f851-f477-4f2d-94bc-35c00d3d5fd8/resourceGroups/Stellar/providers/Microsoft.Compute/galleries/StellarCyberSoftwares/images/Stellar-ModularSensor/versions/<version>" --admin-username azureuser --admin-password P@ssw0rd#2022 --storage-sku StandardSSD_LRS --os-disk-size-gb 128 -
Create inbound security groups for the modular sensor, replacing <resource-group> with the name of your resource group and <NSG NAME> with the name of your network security group
az network nsg rule create -g <resource-group> --nsg-name <NSG NAME> -n StellarPort1 --direction Inbound --protocol Udp --destination-port-ranges 8472 --priority 500
Using Shell Variables to Create the Sensor VM
The az vm create commands in the examples above all specify values for parameters directly in the command. As an alternative, you can also declare shell variables for parameters you commonly reuse and include them in the az vm create command as part of a script.
The same rules for parameters included in an az vm create command also apply when passing variables in a script:
-
The specified
resource-groupmust already exist. -
Any values you supply for the
vnet-name,subnet,subnet-address-prefix, andnsgarguments must exist in the specified resource group.
The example below starts by defining values for many of the parameters in the az vm create command before reading them in as part of the command:
#PowerShell script
#Assign values to variables
$RESOURCE_GROUP="<MyResourceGroup>"
$VM_NAME="<MyVM>"
$VNET_NAME="<MyVNet>"
$SUBNET_NAME="<MySubnet>"
$SUBNET_PREFIX=”<x.x.x.x/x>”
$NSG_NAME=””<MyNSG>”
$IMAGE=”/subscriptions/0e28f851-f477-4f2d-94bc-35c00d3d5fd8/resourceGroups/Stellar/providers/Microsoft.Compute/galleries/StellarCyberSoftwares/images/Stellar-ModularSensor/versions/<version>”
$ADMIN_USERNAME="azureuser"
$ADMIN_PASSWORD="P@ssw0rd#2022"
#Create Modular Sensor VM using variable values
az vm create --size Standard_B12ms --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $VM_NAME --vnet-name $VNET_NAME --subnet $SUBNET_NAME --subnet-address-prefix $SUBNET_PREFIX --nsg $NSG_NAME --image $IMAGE --admin-username $ADMIN_USERNAME --admin-password $ADMIN_PASSWORD --storage-sku StandardSSD_LRS --os-disk-size-gb 128Refer to this article on Microsoft Learn for more information on using variables in the Azure CLI.
Applying a Token to the Installed Sensor
The next step is to obtain and apply the token used to authorize and configure the installed sensor.
Obtaining a Token for the Installation
Tokens are required to authorize and configure the installation of a sensor image downloaded from the DP in the System | Deployment | Sensor Installation page. Tokens point the installed sensor to the correct DP, assign the specified tenant, and authorize the sensor installation.
Use the following procedure to obtain a token in the Tokens tab:
-
Navigate to the System | Deployment | Sensor Installation page and click on the Tokens tab.
-
If a token already exists for the target tenant for the sensor installation, you can either use the Copy button to copy it to the clipboard or use the Download button to download it as a file.
-
Copy the token if you plan on applying it by pasting it into a
set token string <token>command in the CLI. -
Download the token as a file if you plan on hosting the file on an HTTP server and referring to it in a
set token url <token url>command.
Refer to Assigning Tokens for a summary of the different ways in which tokens can be applied to a sensor installation.
-
-
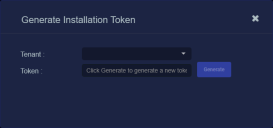
If there is not already an unexpired token for the target tenant, click the Generate button.
The Generate Installation Token dialog appears:
-
Select the tenant for the token from the Tenant dropdown. This is the tenant to which all sensors authorized with this token will be automatically assigned. The dropdown lists all tenants configured for your organization in the System | Tenants page.
-
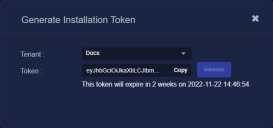
Click the Generate button.
The system generates the token and displays its contents in the Token field. The dialog also updates to display the expiration date for the token, as illustrated below.
-
You can use the Copy button to copy the token to the clipboard immediately, or simply close the dialog and retrieve the token from the Tokens tab later on.
Applying the Token to the Sensor
Tokens are required to complete the installation of a sensor image downloaded from the DP in the Download Image tab.
You apply tokens to sensors as the last step in the overall installation procedure:
- Log in to your new Sensor. The default username/password is aella/changeme. You are immediately prompted to change the password.
-
Apply the token to the installed sensor from the sensor CLI with the
set tokencommand using one of the options in the table below:You only need to use one of the options in the table below. These are just two different ways to do the same thing – apply the token.
Option 1. Copy and Paste the Token String
Copy the token string from the Tokens tab and paste it into the CLI command. The syntax is as follows:
set token string <pasted string>Option 2. Host the Token on an HTTP Server
Download the token as a file from the Tokens tab, upload it to an HTTP server, and reference it in the
set tokencommand. The syntax is as follows:set token url http://<url to token>You can also use an HTTPS server. In that case, the specified URL must also include the username and password for the server using the following syntax:
set token url https://<user:password>@URL> -
The CLI reports that the Sensor token is successfully set.
If you receive an error message instead, it's possible that the token has expired. Refer to the Tokens tab to see the expiration date. If you are using the File technique, it's also possible that an extra space or line may have crept into your text file – check the file to make sure it includes only the token text.
-
Wait a minute or so. Then, verify that the token was successfully applied using any combination of the following techniques:
-
Check the System | Sensors tab in the user interface to see that the sensor has registered itself successfully.
-
Verify that the
show systemcommand shows all services as running. -
Verify that the
show receivercommand displays a receiver. -
Verify that the
show jsoncommand reports some data sent in theBYTE_SENTcolumn.
-
Configuring a Static IP Address (Optional)
By default, the sensor uses DHCP for the management port's IP address. For ease of troubleshooting, however, Stellar Cyber recommends that you reconfigure the management port to use a static IP address. The procedure is as follows:
- Log in to your sensor. The default username/password is aella/changeme, but you changed this when you applied the token in the previous section.
-
You can set IP parameters manually using commands similar to the following (substitute your own IP parameters for the ones shown in bold below):
set interface management ip 192.168.14.100/255.255.255.0
set interface management gateway 192.168.14.1
set interface management dns 8.8.8.8
-
Verify the IP settings with the
show interfacescommand. - Log out with the
quitcommand.