Configuring API Authentication 
This topic describes the authentication required to make calls to the Stellar Cyber API. In general, you will need a user account with sufficient privileges, an API key, and a JSON Web Token created from the API key. See the following sections for details:
If you are trying to authenticate with the API test page found under ? | API Docs, refer to Authenticating with the API Test Page for instructions.
About Scoped API Keys 
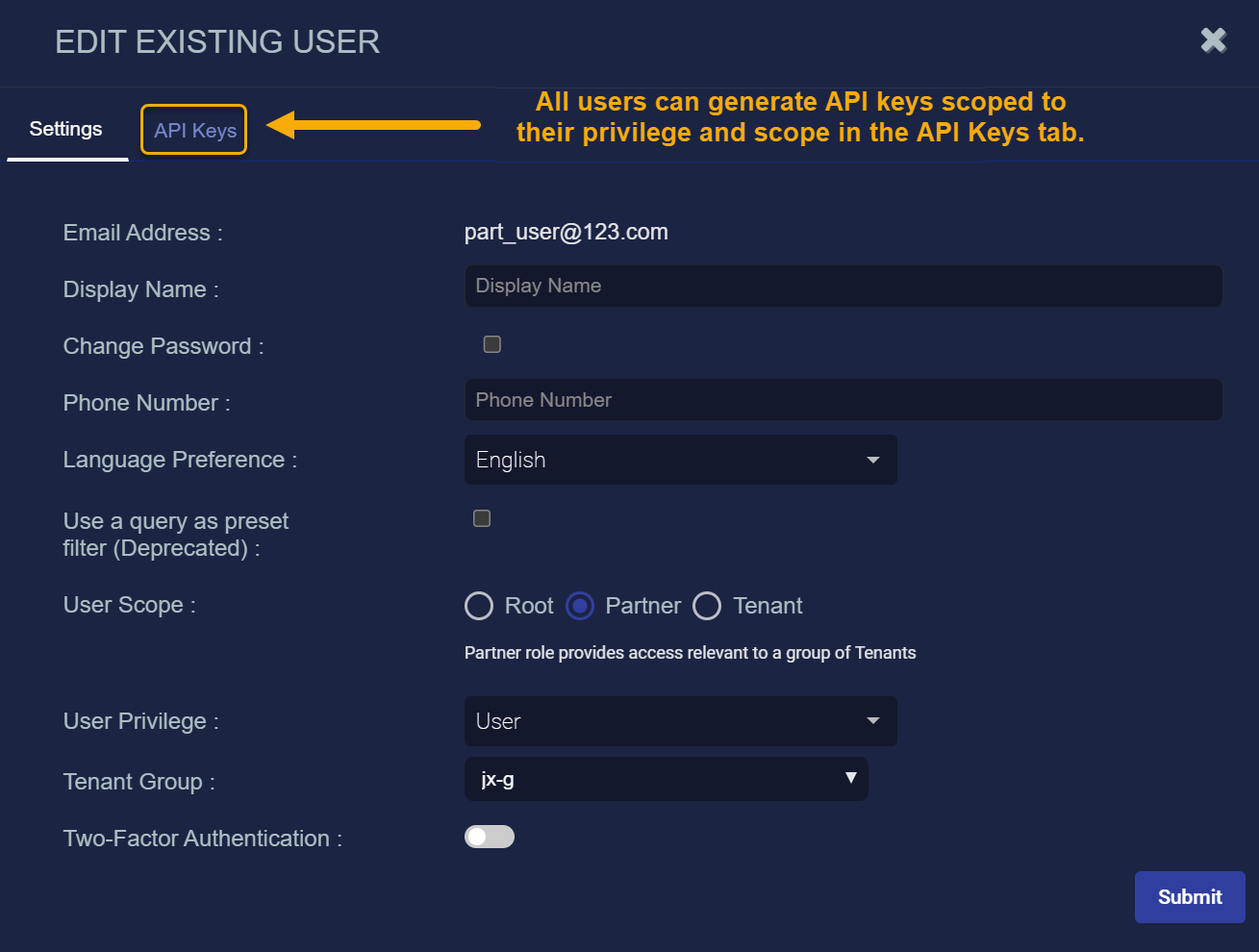
Prior to the 5.5.0 release, public API access was only available to users with Root scope and Super Admin privileges. The 5.5.0 release complements that support with new per-user API keys, scoped to a user's RBAC privileges and tenancy. You can now configure API keys for your own account, regardless of your scope and privileges in the API Keys tab in the Edit User and User Profile dialog boxes, as illustrated below:
Benefits of Scoped API Keys
The new implementation of API keys in 5.5.0 has the following benefits:
-
Respects the industry-standard principle of least privilege, only granting an API key the tools that it needs to perform the job you want it to do.
-
Allows easy breach isolation, with API keys tied to specific users.
-
Enables immediate key revocation to contain exposures quickly and limit the dwell time of any unauthorized access.
Stellar Cyber recommends that you consider creating service accounts scoped with only the RBAC privileges necessary to perform specific tasks. This way you can grant personnel just the access they need to perform specific API tasks.
Managing Scoped API Keys
Both the Edit User and User Profile dialog boxes include an API Keys tab that lets you create and revoke an account's API keys. The keys listed in the API Keys tab are specific to the selected account and are limited by its user scope (tenancy) and RBAC privileges:
-
An account can only make calls to the public API endpoints available to its assigned RBAC privileges.
Certain public API endpoints are restricted to Super Admin users with root scope. Refer to Restricted Public API Endpoints for a list.
-
An account can only access API data available to its user scope and tenancy. For example:
-
A partner user can access data for any of its associated tenants.
-
A tenant user can only access data for its own tenancy.
-
A root user can access data from the entire platform.
-
You use the API keys in the API Keys tab to generate a JSON Web Token for access to the API.
Administrative users can revoke keys for users with lower privileges than their own, subject to the normal limits on tenancy and scope. They cannot, however, create a key for another user.
| Version Number | Account Requirements | Authentication Available |
|---|---|---|
| 5.4.0 | Super Admin users with Root scope | |
| 5.4.0s | Super Admin users with Root scope | |
Restricted Public API Endpoints
The table below lists the public API endpoints that remain accessible only to Super Admin users with root scope. These endpoints do not support user-scoped access:
|
Version 5.5.0 |
Version 5.5.0s |
|---|---|
| /storage-usages | /storage-usages |
| /storage-usages/daily_and_monthly | /storage-usages/daily_and_monthly |
|
/incidents |
/incidents |
|
/entity_usages/entity_list/{scope} |
/entity_usages/entity_list/{scope} |
|
/reset_user |
/reset_user |
|
/ingestion-stats |
/data |
|
/data |
|
|
/update_ser |
|
|
/security_events/{index}/[id|tags|status|comment] |
|
| /insert_ser | |
| /insert_ser_bulk |
Required Privileges to Make API Calls
There are no user account requirements to make API calls. The available public API endpoints are limited by account's RBAC privileges and tenancy.
We recommend creating a Stellar Cyber user dedicated to API calls. That way you can easily track changes made through API calls under System | Users | Activity Log. You can create multiple service accounts, each dedicated to a particular level of API access.
Access to the API is only available using local user accounts. Single-sign on (SSO) users cannot access the API with their SSO credentials.
Necessary Information to Make API Calls
Calls to the Stellar Cyber API typically require a subset of the following information:
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| Email Address | Email address of the admin account making the call. |
| API Key or Token |
Generate an API key or token as follows:
|
| YourStellarCyberServer | The URL or IP address of your Stellar Cyber server. |
Authentication for API Calls
Requests to the Stellar Cyber public APIs can be secured using either of the following techniques:
-
Basic Authentication – With basic authentication, you use only the API key retrieved from System | Users to authenticate API calls.
This is the technique that has been used in previous Stellar Cyber releases and is still available.
-
JSON Web Token Authentication – JWT authentication offers enhanced authentication consistent with industry best practices. With JWT authentication, you use the API key retrieved from System | Users to generate a time-sensitive JWT. See the next section for details on using JSON web tokens.
Generating a JSON Web Token (JWT) from the API Key
Requests to the Stellar Cyber public APIs
JWT authentication offers rapid, scalable, and secure authentication for API calls. They are also time-sensitive, expiring ten minutes after they are generated. Because of this, scripts you write to pull data from the Stellar Cyber API should typically include a section used to refresh the requesting user's JWT.
The sample scripts in this topic include a section that refreshes the JWT using the supplied API Key.
You generate a JWT by sending a request to the public https://<YourStellarCyberServer>/connect/api/v1/access_token API on the DP. The request must include the API Key you created in the API Keys tab in either the Edit User or User Profile dialog box . The API Key acts as a refresh token that you use to generate a new JWT.
For example, the sample Python script below retrieves a JWT and prints it to the screen using the following details:
-
DP – myserver.stellarcyber.cloud
This is specified in the HOST variable at the top of the sample script.
-
API Key from GUI – eyJhbGciOiJNisI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJhcGlfa2V5Ijp7ImtleV9pZCI6ImU5MTRlZCIsInVzZXJfaWQiOiJjN2JkMDI3ZGEzMjc0MDU1YTZkODQ5YTk5N2QxYmUwOCIsIm9yZ19pZCI6IjQ5MGI2MDk2Yjk5ZTQ1ZDY4NTdjOTdjNDA4YjQzMTE4IiwiZXhwIjo0ODk3NzI0MzY3fSwiaWF0IjoxNzQ0MTI0MzY3fQ.ReZlP7DQB4w1UyVw3X1hwppFM4T3lZBxZviHfnVj2Sk
This is specified in the refresh_token variable in the sample script.
#!/usr/bin/python3
import requests
import base64
import json
from urllib.parse import urlunparse
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings()
# Step 1
# Add DP IP/hostname and refresh token from GUI here
HOST = "myserver.stellarcyber.cloud"
refresh_token = "eyJhbGciOiJNisI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJhcGlfa2V5Ijp7ImtleV9pZCI6ImU5MTRlZCIsInVzZXJfaWQiOiJjN2JkMDI3ZGEzMjc0MDU1YTZkODQ5YTk5N2QxYmUwOCIsIm9yZ19pZCI6IjQ5MGI2MDk2Yjk5ZTQ1ZDY4NTdjOTdjNDA4YjQzMTE4IiwiZXhwIjo0ODk3NzI0MzY3fSwiaWF0IjoxNzQ0MTI0MzY3fQ.ReZlP7DQB4w1UyVw3X1hwppFM4T3lZBxZviHfnVj2Sk"
def getAccessToken(refresh_token):
headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer " + refresh_token
}
url = urlunparse(("https", HOST, "/connect/api/v1/access_token", "", "", ""))
res = requests.post(url, headers=headers, verify=False)
print(res.status_code)
return res.json()["access_token"]
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Step 2: Use getAccessToken with supplied credentials to generate JWT
jwt = getAccessToken(refresh_token)
print("------------ jwt -------------")
print(jwt)
print("------------ jwt end -------------")Generating a New JWT as Part of a Script
Because JWTs expire ten minutes after they are generated, you may want to include logic in your scripts similar to the previous code sample to generate and use a fresh JWT every time the script is run.
For example, the code sample below uses the same host and refresh_token as above but includes it as part of a script that pulls the ten most severe cases for a specific tenant. Note the following:
-
The script sets the host and refresh_token in the same places as the previous script (Step 1 in the sample).
-
The script runs the getAccessToken procedure to generate the new JWT (Step 2 in the sample).
-
The script uses the generated JWT to make a call to the cases API in the getCases procedure (Step 3 in the sample). This procedure also includes specific arguments that specify the tenant_id and how many cases to retrieve (10), as well as the order in which to return them (desc).
-
The script also prints the generated JWT to the screen. This, however, is not strictly necessary since the getAccessToken procedure already prints the status code for the call to the access_token API (200 for success; 401 for failure).
#!/usr/bin/python3
import requests
import base64
import json
from urllib.parse import urlunparse
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings()
# Step 1
# Add DP IP/hostname and refresh token from GUI here
HOST = "myserver.stellarcyber.cloud"
refresh_token = "eyJhbGciOiJNisI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJhcGlfa2V5Ijp7ImtleV9pZCI6ImU5MTRlZCIsInVzZXJfaWQiOiJjN2JkMDI3ZGEzMjc0MDU1YTZkODQ5YTk5N2QxYmUwOCIsIm9yZ19pZCI6IjQ5MGI2MDk2Yjk5ZTQ1ZDY4NTdjOTdjNDA4YjQzMTE4IiwiZXhwIjo0ODk3NzI0MzY3fSwiaWF0IjoxNzQ0MTI0MzY3fQ.ReZlP7DQB4w1UyVw3X1hwppFM4T3lZBxZviHfnVj2Sk"
def getAccessToken(refresh_token):
headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer " + refresh_token
}
url = urlunparse(("https", HOST, "/connect/api/v1/access_token", "", "", ""))
res = requests.post(url, headers=headers, verify=False)
print(res.status_code)
return res.json()["access_token"]
def getCases(token):
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer " + token}
url = urlunparse(("https", HOST, "/connect/api/v1/cases?tenantid=817418af76d44358922636e34be9627c&limit=10&sort=score&order=desc", "", "", ""))
res = requests.get(url, headers=headers, verify=False)
print(res.status_code)
return res.json()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Step 2: Use getAccessToken with supplied credentials to generate JWT
jwt = getAccessToken(refresh_token)
print("------------ jwt -------------")
print(jwt)
print("------------ jwt end -------------")
# Step 3: use JWT token to call public API
cases = getCases(jwt)
print("------------ call result of /connect/api/v1/cases -------------")
print(cases)
print("------------ end api results -------------")All API Calls Stored in User Activity Log
Any API request to the public APIs listed here is logged to the User Activity Log with the corresponding user. The request body is also visible by clicking the JSON Data button for the call in the User Activity Log page.